Want to build your own generative AI applications? Here’s a list of AI models to help you get started.
AI models are neural network architectures that perform extremely well on specific tasks. These include convolutional neural network architectures for image classification and segmentation, generative pre-trained large language models, diffusion models for image generation tasks, and
Recently AI models for generative AI applications—for image, speech, text, and more—have become super popular. Which is both due to advances in research and access to high-performance computing.
Here is a quick summary of the popular AI models I’ll be discussing below.
| Model | Key Capabilities |
|---|---|
| GPT-4 | An open-source large language model can be used to build LLM-powered applications |
| LLaMA | Variety of NLP applications, from chatbots to coding assistants |
| Falcon | Open-source large language model can be used to build LLM-powered applications |
| Stable Diffusion | Text-to-image, image inpainting, outpainting, and upscaling |
| DALL-E 2 | Text-to-image generation |
| Whisper | Speech recognition, language translation, and language detection |
| StableLM | Open-source lightweight large language model |
| CLIP | A variety of NLP tasks, such as question answering, summarization, and text generation |
| InternLM | An open-source large language model; can be used to build LLM-powered applications |
| Segment Anything Model | Zero-shot generalization for a variety of image segmentation tasks |
| WaveGAN | Audio generation |
| CycleGAN | Image-to-image translation |
| BioGPT | Biomedical text generation and mining |
From AI art to building a personalized coding assistant, you can build a range of generative AI applications based on your interests. Here, we list some interesting AI models you can explore—along with their key capabilities.
Let’s get started!
GPT-4
From generating the itinerary for your upcoming travel plans to drafting cover letters that fit the job description, ChatGPT has become a part of our day-to-day tasks. GPT-4, its successor, is an even more powerful large language model.
It’s OpenAI’s most powerful AI system with better reasoning capabilities and performance than ChatGPT.
Here’s a tech talk on how GPT-4 works and how you can build applications with it.
You can access the ChatGPT interface with a free OpenAI account. To access GPT-4, however, you should have a ChatGPT Plus subscription.
Here are a few applications you can build with these large language models:
- Custom chatbots
- Improving CRM platforms
- Question-answering on a custom corpus
- Other tasks like summarization and text generation
Next, we’ll go over some open-source large language models.
LLaMA
Meta AI released LLaMA, a foundational large language model with 65B parameters, in February 2023. Subsequently, LLama 2 was released with substantial improvements over the previous release. You can access the following:
- Llama Chat: Fine-tuned Llama 2
- Code Llama: Built on Llama 2; trained on over 500B tokens of code; supports code generation in all of the most popular programming languages
You can download and use the Llama models by requesting access. Check out this tutorial to learn how to use LLama 2 in your Python applications:
Falcon
Falcon is yet another open-source language model by the Technology Innovation Institute (UAE). All the models in the Falcon LLM suite are open source and are available for open access. So you can use them to build LLM-powered applications.
Currently, there are four model sizes: 1.3B, 7.5B, 40B, and 180B. to perform better than on several benchmarks the 180B model was trained on a dataset of 3.5T tokens. The Falcon LLM performs at par with other leading open-source LLMs.
The Falcon 180B open-source LLM achieves performance close to that of GPT-4. Check out this tutorial that covers Falcon 180B, how you can use it, the hardware requirements, and how to compare to GPT-4:
Stable Diffusion
Stable Diffusion a text-to-image model for image generation and other creative AI applications. It can also be used for image upscaling and inpainting.

Stable Diffusion XL, released in July 2023, offers several improvements, including:
- generating descriptive images from much shorter prompts
- the ability to generate support text within images
- image inpainting and outpainting tasks
- interacting with a sourced image to generate variants
If you want to learn how diffusion models work—the method behind the magic—check out How Diffusion Models Work, a free course by DeepLearning.AI.
DALL-E 2
DALL-E 2 from Open AI is another popular text-to-image generation model. You can use it to generate realistic images and art from text—natural language description.
It can be used for the following tasks:
- image generation from text prompts
- image inpainting and outpainting
- generating variations of an image
You can access DALL-E 2 via the OpenAI API or the OpenAI labs web interface.
Whisper
Open AI’s Whisper is a speech recognition model that can be used for a multitude of applications, including:
- language identification
- speech recognition tasks such as transcription of audio files
- speech translation
Here’s a tutorial on how to convert speech to text using the OpenAI Whisper API:
To try out the model, you can install whisper (openai-whisper) using pip and accessing the API from within a Python script to transcribe audio files. Further, you can use other large language models to summarize the transcript and build an audio file → summary pipeline.
StableLM
StableLM is an open-source LLM suite from Stability AI. The 3B and 7B parameters are currently available. Subsequent releases will include larger models with 15B – 65B parameters.
So, if you want to experiment with lightweight, open-source LLMs in your applications, you can try out StableLM.
CLIP
CLIP stands for Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training. It’s a neural network, a multi-modal model, trained on a large dataset of (text, image) pairs. The model leverages natural language data, tries to learn—from the natural language descriptions—the semantics of the images. The CLIP model is capable of predicting the most relevant text given an image.
With CLIP, you can perform zero-shot image classification—without expensive pre-training and fine-tuning. Further, you can leverage the capabilities of CLIP and vector databases to build interesting applications in:
- text-to-image and image-to-image search
- reverse image search
Segment Anything Model
Image segmentation is the task of identifying pixels belonging to a specific object within an image. Meta AI released Segment Anything Model (SAM) that can be used to segment any image and cut out objects from them.
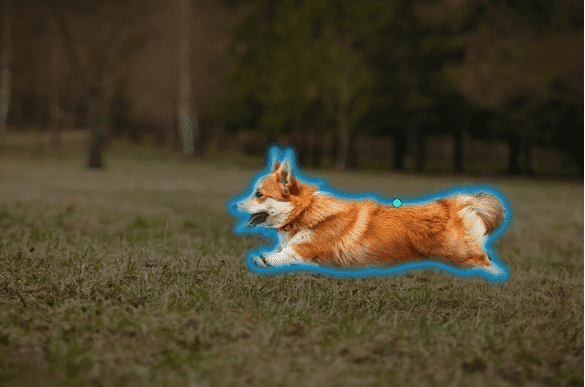
You can use prompts to specify what to segment in an image. SAM currently supports the following prompts: bounding boxes, masks, and foreground and background points. The model also has excellent zero-shot generalization performance on previously unseen images. So no explicit training is required.
Try out the SAM model in your browser!
InternLM
InternLM is an open-source language model. You can try out the 7B base model and the open-source chat model. The model supports a context window of 8K. Additionally, InternLM supports code interpreter and function calling capabilities.
InternLM is also available in the HuggingFace transformers library. You can leverage the lightweight pre-training framework. It also supports building and deploying applications using LMDeploy. So, you can build end-to-end generative NLP applications with InternLM.
WaveGAN
WaveGAN is a model for audio generation. It helps synthesize raw audio from samples of real audio data.
You can train WaveGAN on a dataset of arbitrary audio files and synthesize audio without extensive preprocessing.
CycleGAN
So far, we’ve covered speech-to-text, text-to-image, and other models for various natural language processing tasks. But what if you want to perform image-to-image translation? Here, you can use CycleGAN to learn a mapping from the source domain to the target domain to perform image-to-image translation.
For example, given the image of a lakeside during winter, you may want to translate the same image when the season is summer. In the image of a horse, you may want to replace the horse with a zebra while retaining the same background. CycleGAN is well-suited for such tasks.
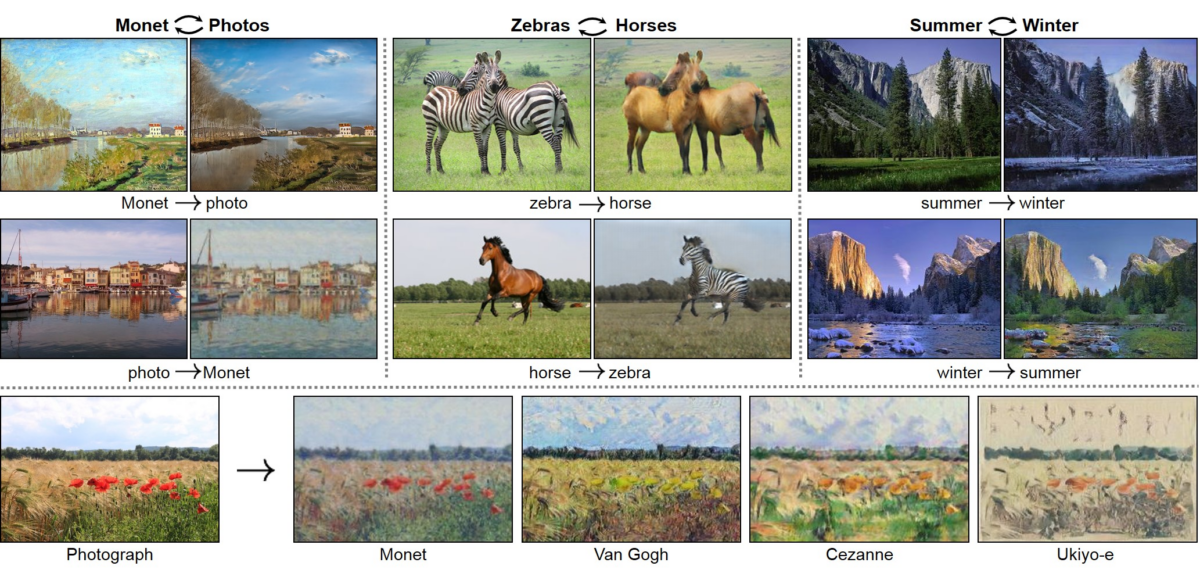

You can find the PyTorch implementations of CycleGAN on GitHub.
BioGPT
BioGPT from Microsoft is a transformer model you can use for biomedical data mining and text generation applications. It uses the sequence-to-sequence model implementations provided by fairseq.
Fairseq from Facebook research (now Meta AI) is a toolkit that provides implementations of sequence-to-sequence models for tasks such as:
- language modeling
- translation
- summarization
Both the pre-trained models and fine-tuned model checkpoints are available. You can download the model either from the URL or from the HuggingFace hub.
The BioGPT models are also part of the HuggingFace transformers library. So, if you’re working in the biomedical space, you can use BioGPT to build domain-specific applications.
Wrapping Up
I hope you found a few useful models that you can build generative AI applications with. Though this list is not exhaustive, we’ve covered some of the most popular models you can use to build apps for text and audio generation, speech-to-text transcription, image search, and more.
When you’re building applications using large language models, you should be aware of the common pitfalls, such as factually incorrect information and hallucinations. And you may face limitations when fine-tuning models as the fine-tuning process is often resource-intensive.
So if you’re a developer, it’s time to join the AI revolution and start building interesting AI applications! You can try out these models in Google Colab or other collaborative data science notebooks.