.tar.gz files are commonly known as tarballs.
The term “tarball” is derived from two components: “.tar” representing the Tape Archive format and “.gz” denoting the gzip compression algorithm.
.tar.gz files are widely used for source code Distribution & Web Server Deployment due to their versatile nature and efficient compression.
First, let’s understand what the difference between .tar & .tar.gz file format and the benefits of it.
Then we’ll jump into the step-by-step process of unzipping on both Linux and Windows platforms.
Let’s get rolling!
.tar Files
The .tar extension stands for “tape archive.”
A .tar file is an archive that does not undergo any compression.
It just bundles files & directories together while preserving their file structure and metadata. This means it takes all the specified files and puts them together into one container.
But it does not compress the data, which results in a larger file size compared to compressed formats.
.tar.gz Files

These files are a combination of two steps: Archiving and Compression.
The .tar.gz extension indicates a file that is a .tar archive and compressed using the gzip utility.
Gzip compression reduces the overall file size, which makes it more efficient for distribution, backup, and storage purposes.
This format is common in the Unix/Linux world and is widely used to create compressed archives.
This compression is lossless – that means no data is lost during the compression process, and the original files can be fully restored upon extraction.
Also read: tar Command Examples for Sysadmin and Developers
.tar vs .tar.gz Files

Both these file archives are used for binding multiple files and directories into a single file, but they just differ in their compression methods. Here are some general differences between the .tar and .tar.gz files.
| Feature | .tar Files | .tar.gz Files |
| Compression | No compression, files are stored as it is. | Compressed using gzip |
| File Extension | .tar | .tar.gz or .tgz |
| Compression Ratio | None | High compression ratio |
| Ideal Use | Archiving only | Distribution and Archiving |
| File Size | Larger | Smaller |
| Extraction | Quick | Slower (due to decompression) |
| Use Case | Archiving files, creating backups | Efficient data transfer, software distribution |
Benefits of .tar.gz Files
These files offer several benefits that make them a popular choice for archiving and distributing files. Here are some of the key advantages:
Preservation of File Attributes
.tar.gz files retain important file attributes such as permissions, timestamps, and ownership information. When the archive is extracted, these attributes are restored. That means they maintain their original characteristics.
File Organization
As already discussed, The .tar format allows bundling multiple files into a single file which makes it easier to organize related data or complex directory structures into a single archive.
This simplifies file management and reduces the risk of data loss during transfers.
Checksum Integrity
gzip compression uses a checksum to make sure data integrity. When you extract files from a .tar.gz archive, the checksum is automatically verified to detect & handle any potential data corruption.
Open Source Standard
The .tar.gz format is an open-source standard. That means it is not tied to any specific proprietary software.
Incremental Backups
These files can be used in incremental backup strategies – where only new or modified files are added to the archive.
Extracting .tar.gz Files for Linux
To unzip the .tar.gz files, you’ll need to use specific commands and tools depending on your operating system. Let’s explore the extraction process for both Linux & Windows platforms.
Linux systems come with built-in tools that can extract .tar.gz files easily. The most commonly used command-line tool for this purpose is tar. Follow these steps:
Method 1: Using the Command Line
Step 1: Open a terminal.
Step 2: Navigate to the directory where your file is located using the ‘cd” command. For example, To navigate to the “Downloads” folder:
cd ~/DownloadsStep 3: And the next step is to unzip the .tar.gz archive format. For that, just use the following command
tar -zxvf your_file.tar.gzThe options used here are:
z: Use gzip to decompress the file.
x: Extract the files.
v: Verbose mode (optional but provides detailed output).
f: Specify the filename to be extracted.
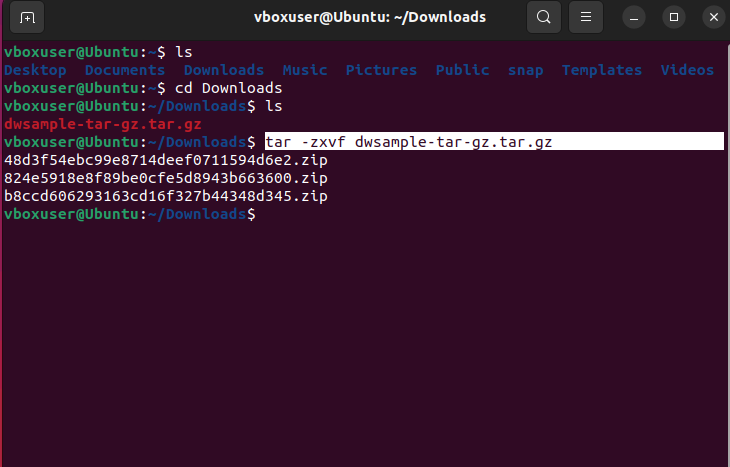
You can notice in the above image that the archive files are extracted in the same working directory.
Method 2: Using File Manager (GUI)
Step 1: Open the file manager (e.g., Nemo, Nautilus, Dolphin).
Step 2: Right-click the .tar.gz file.
Step 3: Select the “Extract Here” or “Extract to” option – depending on whether you want the files to be extracted in the same location or a different folder.
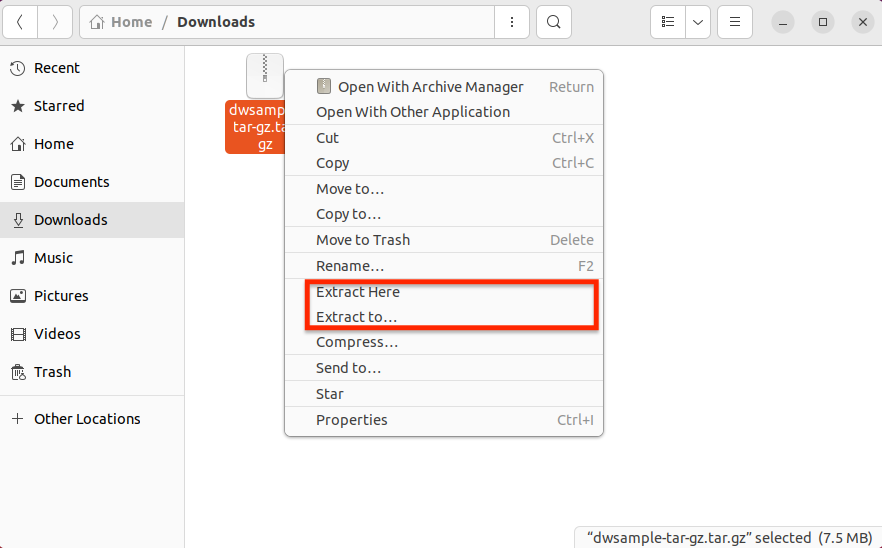
The files will be extracted to the selected location.
Extracting .tar.gz Files for Windows
You can easily extract .tar.gz files using third-party tools like 7 zip and Winrar on the Windows system.
Method 1: Using 7-Zip
7-Zip is a free and open-source tool with high compression ratios & supports a wide range of archive formats. It offers AES-256 encryption to protect sensitive data within archives. Users can utilize the 7-zip command-line interface for automated & scripted extraction tasks.
It also integrates with the Windows Explorer context menu, which enables users to create and extract archives directly from the right-click menu.
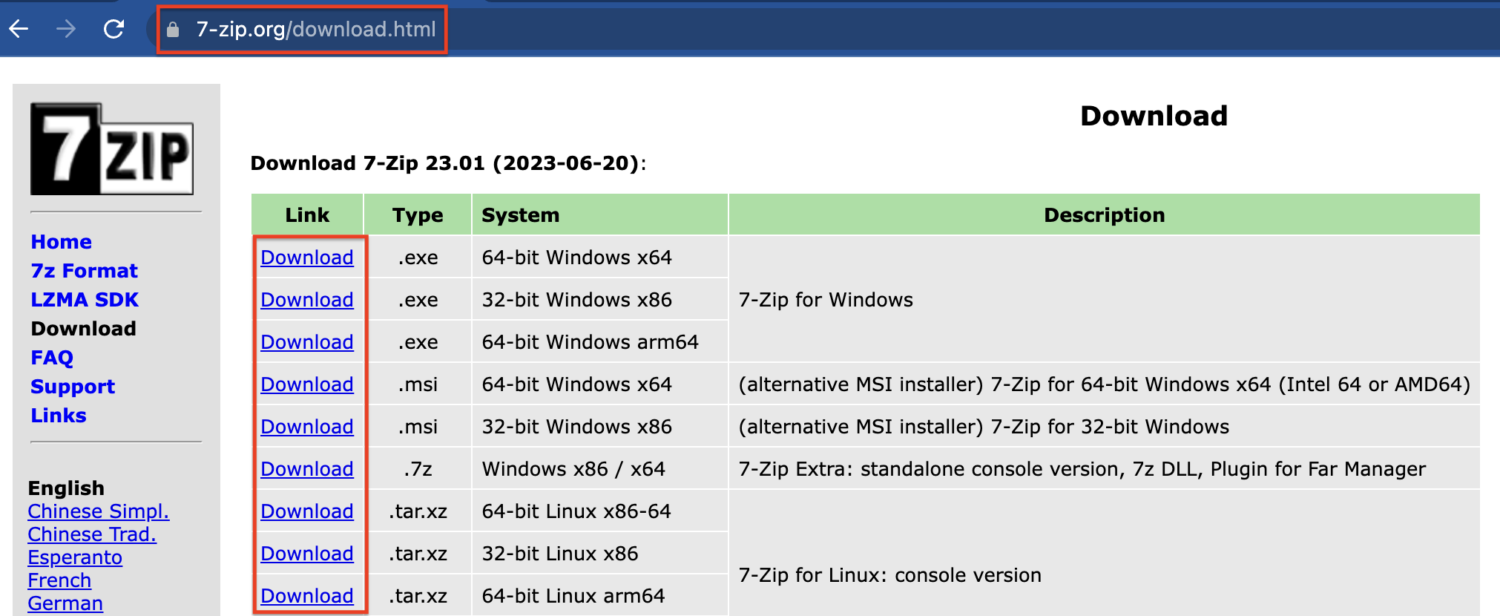
Step 1: Visit the official website & download the suitable version for your Windows OS.
Step 2: Install 7-Zip by following the on-screen instructions.
Step 3: Navigate to the directory and right-click on the file you want to extract.
Step 4: Hover over the 7-Zip option, and choose “Extract Here” from the context menu.
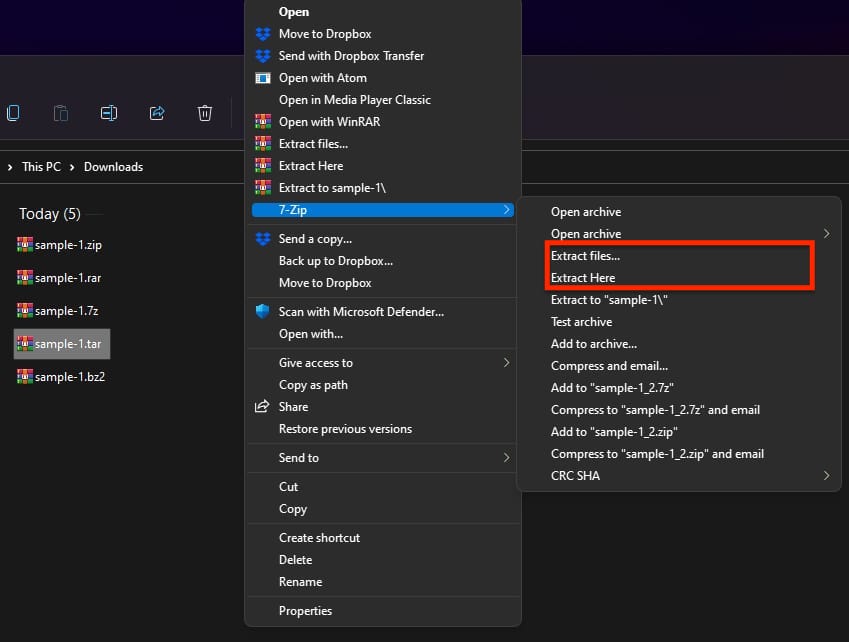
The extraction method is precisely the same for tar files that have compression, such as.tar.gz,.tar.bz2, and others.
Method 2: Using WinRAR
WinRAR is a popular file compression & archive utility software. It allows users to create, view, and extract files in various archive formats, including its native .RAR format as well as other common formats like .ZIP, .7z, ISO, .TAR, and more.
Step 1: WinRAR comes pre-installed on almost every Windows system. In case it’s missing, download and install from the official website.
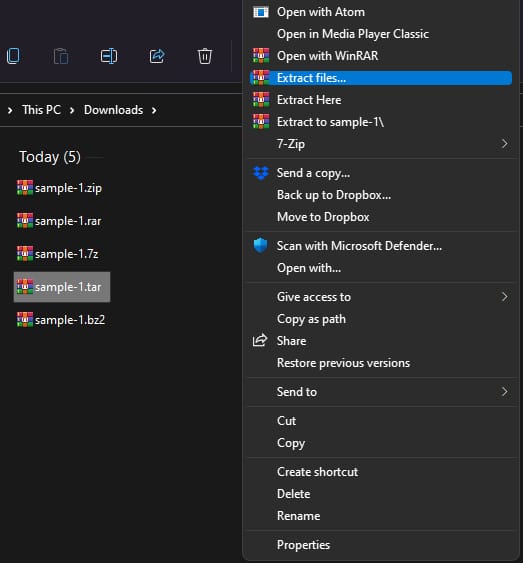
Step 2: Right-click on the file and then select “Extract Here” to extract the contents of the archive into the same directory or you can also choose the desired location.
WinRAR is distributed as shareware. That means users can download and use it for free during a trial period. Also, its trial version does not have time limitations, and users can still use it even after the trial period has expired, with occasional reminders to purchase the license.
Author’s note✍️
.tar.gz files offer an organized way to store & distribute multiple files while saving disk space.
Whether you prefer command-line tools or graphical file archivers, the extraction process is pretty simple.
In Linux, users have multiple ways to extract .tar.gz files – through the terminal and graphical file archivers. The terminal method is only recommended for those comfortable with command-line interactions, while graphical file archivers provide a user-friendly experience and are good for beginners.
On the other hand, Windows users can rely on third-party file archiver tools like 7-zip or WinRAR to effortlessly extract files.
You may also be interested in learning about the best WinZip alternatives to compress files.

