One of the most important ways you can make use of your Linux PC is through files.
Almost every file that you directly work on in the Linux terminal can be manipulated as a text file. This includes configuration files, log files about various services and processes in the system, and script files that come bundled with the Linux Distribution of your choice or which you write yourself.
Knowing how to quickly view the content of these files in the Linux terminal is an invaluable skill that not only saves you time but also helps you learn more about the system. This tutorial will show you how to view these kinds of files in the Linux terminal.
cat
The cat command is a simple and extremely useful command for viewing file contents on Linux.
You can use the cat command to quickly print file content to the standard output in the terminal or alternatively concatenate the output.
The syntax for the cat command is as follows:
$ cat [OPTION] [FILE1] …For example, if you have a file called simple-list.txt, which contains a list of some items, you can view the contents of this file by using the command
$ cat simple-list.txtFor example:
$ cat simple-list.txt
bananas
strawberries
grapes
apples
watermelons
oranges
blueberries
lemons
peaches
avocados
pineapples
cherries
cantaloupe
raspberries
pears
limes
blackberries
clementine
mangoes
plums You can also list multiple files at the same time to get the output of all files in the terminal at once, as shown below:
$ cat testfile1.txt testfile2.txt
these are the contents of testfilel.txt.
and this is the end of testfilel.txt
these are the contents of testfile2.txt.
and this is the end of testfile2.txtnl
If you want to be able to see the line number for each line in a file, the nl command does exactly that. You can use this command in the same way as the cat command, and the only difference is that nl has line numbers enabled by default.
Using the cat command, you can get the same result with the -e option. Here is an example output of the same simple-list.txt file output with nl
$ nl simple-list.txt
1 bananas
2 strawberries
3 grapes
4 apples
5 watermelons
6 oranges
7 blueberries
8 lemons
9 peaches
10 avocados
11 pineapples
12 cherries
13 cantaloupe
14 raspberries
15 pears
16 limes
17 blackberries
18 clementine
19 mangoes
20 plums
The line numbers can be changed to be left justified by using the -nln option. There are other options as well you can use with the nl command, listed under man nl
more
So far, you have needed to scroll through the output using your mouse scroll wheel or Shift+Page-up and Shift+Page-down buttons on the keyboard.
However, more command provides a much easier way to view longer files that do not fit completely within the terminal window.
The same simple-list.txt file is shown when viewed through more commands:
Navigation in the viewing window of more commands can be either line by line or page by page. You can use Enter key to navigate by one line at a time or the Space key to navigate by one page at a time.
The B key is used to go back to the previous page. More command also tells you when you reach the end of the file as well, as shown below:
You can quit the viewing window of more commands at any time by pressing q, which returns you to the terminal screen. In this way, more commands can be used to view long config or log files without breaking the flow of the terminal.
less
Less is a more modern take on more command. Back when fewer commands were introduced in the Linux ecosystem, most commands did not support scrolling back up.
In addition to letting users scroll up and down, less command also supports horizontal scrolling, supports better handling for binary files, and can perform a search through text.
Let’s look at our simple-list.txt file through less:
$ less simple-list.txt
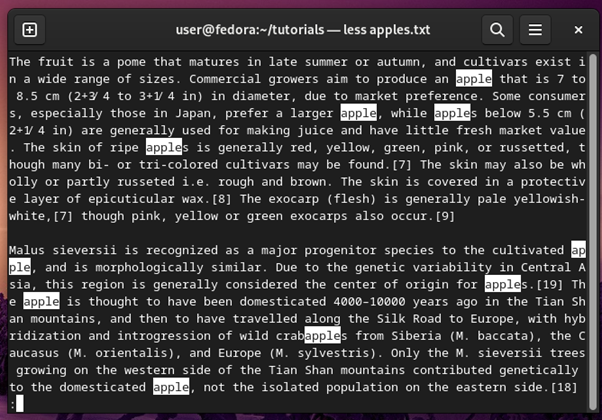
You can use arrow keys on the keyboard to navigate, in addition to the navigation keys for more commands. While you are in the viewing window of less, you can use /word to search through the file contents for word.
This is shown in the screenshot below where the user searches for apple in the file contents:
Less command also supports more advanced features such as being able to view file contents at the first occurrence of a specific word. To do this, the command syntax is as follows:
$ less +/target-word /path-to-fileFor example, to open the apples.txt file at the first occurrence of the word cultivar, the following command would be used:
$ less +/cultivar apples.txthead
If you just want to quickly view the first ten lines of a file, you can do that through
The head command as shown below:
$ head simple-list.txt
bananas
strawberries
grapes apples
watermelons
oranges
blueberries
lemons
peaches
avocadosBy default, only the first ten lines are shown in the terminal, but you can change the number of lines displayed by using the -n option, as shown below:
$ head -n 5 simple-list.txt
bananas
strawberries
grapes
apples
watermelonsSimilarly, the -c option can be used to print a specific number of bytes from the file to the terminal.
tail
The tail command works like the head command, with the only major difference being that it shows the last ten lines of the file instead of the first ten lines.
$ tail simple-list.txt
cherries
cantaloupe
raspberries
pears
limes
blackberries
clementine
mangoes
plums
tangerines $ tail -n 5 simple-list.txt
blackberries
clementine
mangoes
plums
tangerinesIn addition, both head and tail commands can be used with other file viewing commands shown in the tutorial to produce better output for users.
For example, the nl command can be used to first show the file with line numbers. Then the result can be piped to less to view the last three lines of the file, as shown below:
$ nl simple-list.txt | tail -n 3
19 mangoes
20 plums
21 tangerines 
Frequently asked questions about viewing Linux files
You can check the type of a file through the file command, the syntax of which is as follows:$ file [OPTIONS] target-file
You can combine multiple commands through piping to not only search through big log files but to display the search result in a well-organized output.
For example, using grep with nl and tail, you can find out when was the last few times a specific file was requested on your web server, as shown below:$ nl /var/log/apache/mywebsite.log | grep target-file.jpg | tail -n 5
The above command will show the last file times target-file.jpg was requested on your web server.
The space key is used to scroll down a full page with more and fewer commands.
To scroll down line-by-line in less, use the Enter key on the keyboard.
To scroll back up a page, use the b key.
To search for a specific word in the contents of the file you are currently viewing in more or less, use the syntax /word-to-search.
You can use the general command xdg-view, or any variant of it for the specific distribution you have installed, for example, gnome-view or kde-view, to open a rich text or image file.$ xdg-view enwiki.png
This will open the file in the default application for the target file type.

