Being an avid user of open-source tools, I know how painful it can be to find the right open-source firewall for your application or network. Sometimes, open-source firewall code is outdated or lacks documentation and community support. Other times, the firewall has compatibility issues.
To help you overcome these challenges, I have researched 20+ popular solutions and shortlisted the top 11 open-source firewalls in this post.
This open-source firewall curation is divided into two sections—open-source network firewalls and open-source web application firewalls (WAFs)—to help you pick the right solution based on your requirements.
- Open-source Network Firewalls
- 1. pfSense
- 2. IPFire
- 3. OPNsense
- 4. SmoothWall
- 5. Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW)
- 6. ConfigServer Security and Firewall (CSF)
- 7. Endian Firewall Community (EFW)
- Open-source Web Application Firewall
- 8. OWASP ModSecurity
- 9. WebKnight
- 10. Shadow Daemon
- 11. BunkerWeb
- Show less
Open-source Network Firewalls
Let’s take a look at the best open-source Network Firewalls first!
1. pfSense
pfSense software is a free, open-source, customized distribution of FreeBSD. Hosted and developed by Rubicon Communications (in business as Netgate), pfSense has multiple use cases. You can use it as a firewall, router, VPN, IDS/IPS, and more with some add-on packages.

I’ve thoroughly checked the pfSense documentation and found that it has rich resources for each use case. So you will not face any issues setting up and using the pfSense firewall.
pfSense Features
- Stateful packet inspection (SPI)
- IP/DNS-based filtering
- Anti-spoofing rules to block packets with false addresses
- Captive portal guest network
- Time-based rules
- In-bound and out-bound network address translation (NAT)
- Connection limit policy
You can install pfSense on your PC, virtual machine, and hardware for Netgate. It is also available on the Azure and AWS marketplaces.
pfSense Community Edition is free. But pfSense+ is a commercial product that runs on Netgate hardware. I didn’t notice much difference between pfSense and pfSense Plus, except that pfSense Plus includes professional support.
pfSense looks promising and worth a try. You can also run it on a virtual private cloud. Consider Kamatera if you want to host pfSense there.
2. IPFire
IPFire is an open-source Linux-based firewall operating system designed to protect a network against evolving cyber threats. It provides a comprehensive feature set that allows you to customize and tailor the firewall to meet your unique network requirements for a personalized and secure setup.

The platform is community-driven, where users and developers collaborate to share insights and innovations, continuously improving the system.
IPFire Features
- Network segmentation with Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) and guest network setup
- Real-time stateful packet inspection for threat detection
- Secure remote connectivity for employees and partners
- Easy web-based management with one-click access
- Real-time graphs and detailed network insights
What I also liked is that IPFire is not just a firewall. It can support various functions related to network security, VPN, intrusion prevention system, web proxy, and more.
3. OPNsense
OPNsense is a FreeBSD-based firewall and routing system, operating as a fork of pfSense and m0n0wall. It targets various markets, such as schools, remote offices, the hospitality industry, etc.
I’m impressed with OPNsense’s commitment to address evolving security threats. It offers weekly security updates and releases two major updates each year, helping businesses schedule upgrades. Each release follows a roadmap with clear development goals.

I also liked its System Health feature, which provides modern RRD graphs with the ability to zoom in and export data easily.
Here is a Reddit user who is satisfied with OPNsense’s offering. 👇
Comment
byu/No_Blood_5393 from discussion
inopnsense
OPNsense Features
- Stateful Inspection Firewall
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention
- Virtual Private Network (IPsec, OpenVPN, PPTP)
- Two-factor Authentication
- High Availability & Hardware Failover
- Dynamic DNS
- Built-in reporting and monitoring tools, including RRD Graphs
4. SmoothWall
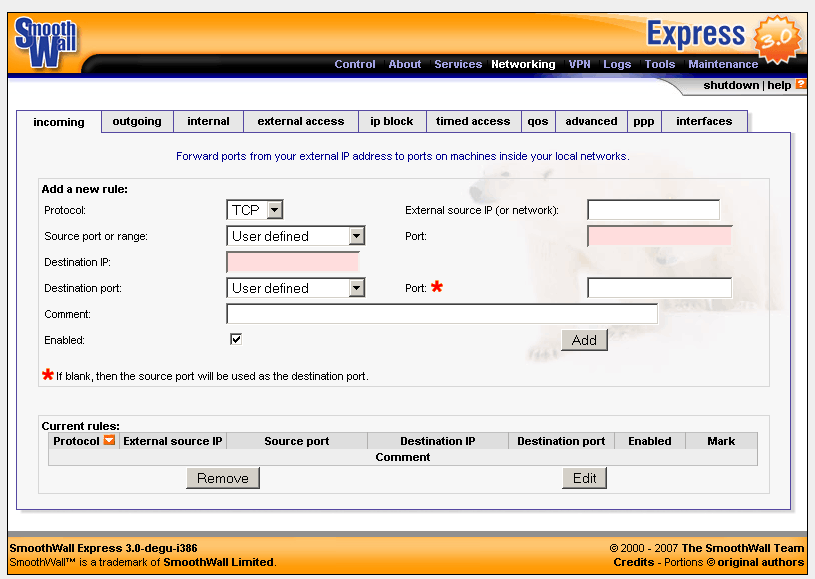
The SmoothWall Open Source Project started in 2000 to create and manage SmoothWall Express, a free firewall. It has a secure Linux-based operating system and a simple web interface for easy management.
Since it’s an open-source tool that offers community support, its community size is a massive advantage. SmoothWall has a strong community of 18,000+ members, including moderators and admins, who are ready to help with questions and feedback
As shown in the screenshot below, it’s easy to add rules in SmoothWall.
5. Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW)
UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) is a firewall management tool for Linux. It simplifies managing iptables (the underlying firewall) by providing an easy-to-use command-line interface.
The tool helps control incoming and outgoing network traffic with simple commands to allow or block connections. It supports both IPv4 and IPv6.
6. ConfigServer Security and Firewall (CSF)
ConfigServer Security and Firewall (CSF) is a free, advanced firewall for Linux servers. It provides a simple way to manage firewall rules and improve server security.
The tool includes intrusion detection, login failure tracking, IP blocking, and port control. It also integrates with popular control panels like cPanel and DirectAdmin.

CSF supports RedHat Enterprise (v7 to v9), CentOS (v7 to v9), RockyLinux (v8 to v9), CloudLinux (v7 to v9), AlmaLinux (v8 to v9), and more. And you can run it on leading virtual servers, such as VMware, Xen, KVM, and Virtual Box, among others.
You can integrate CSF with control panels like cPanel, DirectAdmin, InterWorx, CWP (CentOS Web Panel), VestaCP, and Webmin.
CSF Features
- Checks for login authentication failures
- SSH login notification
- SU login notification
- Excessive connection blocking
- Block traffic on unused server IP addresses
- Pre-configured settings for Low, Medium, or High firewall security
I like its Country Code Blocking feature, which lets you deny or allow access by ISO country code.
7. Endian Firewall Community (EFW)
Endian Firewall Community (EFW) is a Linux-based security software that can turn your old hardware into a full-featured Unified Threat Management (UTM) solution. It includes features like firewall, VPN, IPS/IDS, antivirus, and web filtering, helping protect your network from threats. Its user-friendly interface makes it easy to set up and manage, even for non-technical users.

The platform lets you block/allow traffic by country. You can set time-based rules for the time of day or day of the week. EFW can also protect your network from DoS & SYN/ICMP flood attacks.
It is powered by deep packet inspection technology to detect and block advanced threats.
EFW Features
- Protects the network from internet threats while managing internal and external access.
- Analyzes traffic flows to block internal and external threats.
- Provides secure remote access and connects multiple offices through encrypted tunnels.
- Filters out spam, phishing, and malicious emails to protect business communication.
- Provides real-time and historical insights into network traffic.
Open-source Web Application Firewall
Now that we’ve discussed open-source network firewalls in detail, it’s time to move to open-source Web Application Firewalls. Check them out below!
8. OWASP ModSecurity
ModSecurity is an open-source web application firewall engine that helps protect websites by monitoring and controlling HTTP(S) traffic. Its flexibility and capabilities have given it the moniker of the “Swiss Army Knife” of WAFs.

The tool uses a flexible programming language to protect web applications from various attacks. It can monitor and log HTTP traffic and analyze it in real time. It protects millions of websites, making it one of the most popular WAF tools available.
I like ModSecurity because it’s flexible and allows you to create your own security rules. It supports different security models, which gives you control over how you protect your applications.
- Negative security model blocks known bad requests, which helps stop many automated attacks.
- Positive security model only accepts known good requests, which is useful for stable applications.
- Virtual patching lets you fix security issues from the outside without changing the app’s code.
- Extrusion Detection helps prevent sensitive data leaks by monitoring outgoing traffic.
9. WebKnight
WebKnight is an open-source Web Application Firewall (WAF) that protects IIS (Internet Information Services) servers. It helps prevent attacks by blocking known vulnerabilities and zero-day exploits.
It analyzes HTTP requests for protocol violations and unusual parameters that could harm the application. WebKnight also scans for OWASP Top 10 attack patterns and other threats identified since 2002.
It’s released under the GNU General Public License (GPL), making it free to use and modify.
WebKnight Features
WebKnight offers protection from the following attacks:
- SQLi
- XSS
- CSRF/XSRF
- Parameter Pollution
- Encoding Exploits
- Bad Robots
- Leeching and Hot Linking
- DoS Attacks
- Information Leakage
The tool provides real-time insights into ongoing attacks, which helps your blue team (defenders) monitor and respond to threats. It can also help meet PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) requirements by protecting against web-based vulnerabilities.
10. Shadow Daemon
Shadow Daemon is a web application firewall that analyzes and stores web requests at the application level. It detects and blocks malicious traffic before it reaches the server.
It offers protection from XML injections, code injections, SQL injections, command injections, cross-site scripting, backdoor access, and more.
11. BunkerWeb
BunkerWeb is an open-source Web Application Firewall (WAF) and web server based on NGINX. It protects web services with secure default settings and integrates easily with Linux, Docker, Swarm, and Kubernetes. It’s fully configurable through a user-friendly web UI or CLI, which makes it simpler to manage firewall settings.
It protects your web application from various threats, including, but not limited to, SQL injection attacks, XSS, and DDoS attacks.
In addition to the basic WAF functionalities, BunkerWeb offers advanced protection features, such as integration with third-party tools, custom rule creation, and support for extensible plugin system.
After exploring the above open-source web application firewalls, you may want to check these commercial web application firewalls that offer advanced features and quick support.
5 Disadvantages of Open-Source Firewall
Here are the top five disadvantages of open-source firewalls.
- Limited Support: Open-source firewalls come with community-based support that is often slower or less reliable.
- Complex Setup: It is quite challenging to configure and maintain open-source firewalls without proper technical knowledge.
- Frequent Updates: Keeping up with patches and updates requires manual effort.
- Performance Issues: Some open-source firewalls struggle to handle high traffic volumes or complex rules efficiently.
- Limited Features: Some advanced features (like AI-based threat detection) are often missing in open-source firewalls.
What Is the Difference Between a Network and a Web Application Firewall?
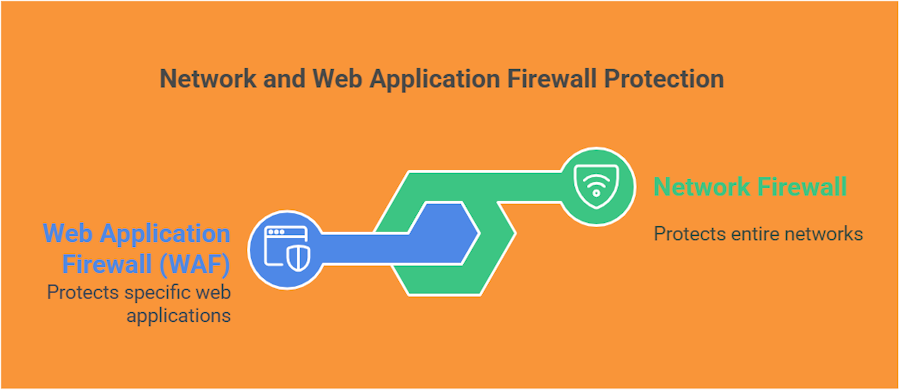
A Network Firewall protects an entire network by filtering traffic at the network layer (Layers 3 and 4 of the OSI model). It controls inbound and outbound traffic based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols. This type of firewall helps prevent unauthorized access, DDoS attacks, and malware from entering or leaving the network. It is suitable for protecting internal networks and data centers.
On the other hand, a Web Application Firewall (WAF) protects specific web applications by analyzing HTTP and HTTPS traffic at the application layer (Layer 7). It detects and blocks threats like SQL injection (SQLi), cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). A WAF inspects the content of requests and responses, providing tailored protection for web applications and APIs.
While network firewalls secure the infrastructure, WAFs focus on protecting web applications from application-level vulnerabilities. Many businesses use both for layered security.
What Is the Difference Between a Stateless and a Stateful Firewall?
A Stateless Firewall uses predefined rules, such as IP addresses, ports, and protocols, to filter traffic without tracking the state of connections.
On the other hand, a Stateful Firewall keeps track of active connections and checks if incoming packets are part of an existing conversation. It remembers the data flow between two devices and decides whether to allow or block packets based on that ongoing connection.
Check out our take on stateful vs. stateless firewalls to learn more!
Conclusion
Firewalls protect your network and applications from unauthorized access and cybersecurity attacks. So you must use a reliable firewall. If you have a limited budget, explore the above-mentioned open-source firewalls and pick the one that meets your security needs.
For businesses with bigger budgets, I recommend exploring managed firewalls since they offer advanced features and prompt security support, and you don’t need in-depth technical knowledge to use them.
-
 EditorAnirban Choudhury is as an editor at Geekflare, bringing over 7 years of experience in content creation related to VPNs, Proxies, Hosting, Antivirus, Gaming, and B2B2C technologies.
EditorAnirban Choudhury is as an editor at Geekflare, bringing over 7 years of experience in content creation related to VPNs, Proxies, Hosting, Antivirus, Gaming, and B2B2C technologies.


