Cyber attacks, including the ever-present threat of the evil twin attack, are becoming more popular with the advancement of technology and connectivity.
Hence, every individual and organization must understand social engineering techniques and how evil twin attack aids in social engineering.
This article will explain the evil twin attack and its detection and prevention.
What are Evil Twin Attacks?
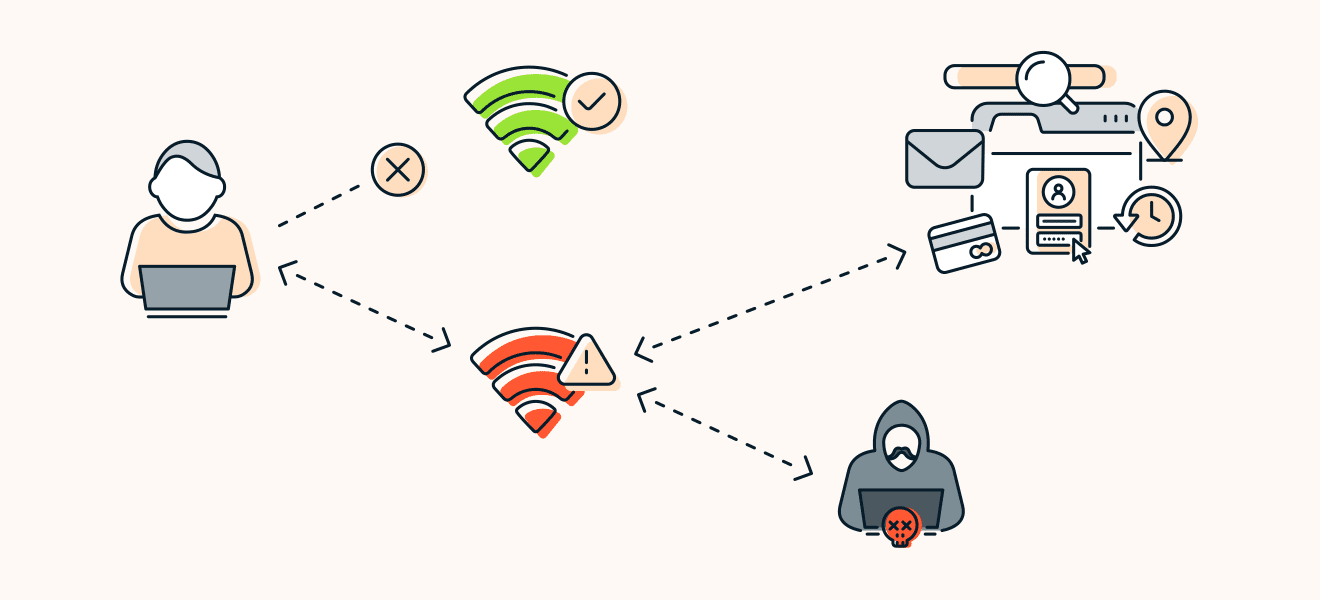
The Evil Twin Attack is a wireless LAN version of a phishing attack. An evil twin attack is a rogue WiFi access point that seems genuine but eavesdrops on wireless communication. This malicious WiFi access point deceives the user into connecting to it.
This attack usually happens in public places such as hotels, airports, railway stations, libraries, or cafes. The evil twin attack leads to data theft, unauthorized access, and other cyber crimes.
How Does the Evil Twin Attack Work?
Step I
The cyber attacker finds a public place to perform the attack, like a hotel, cafe, airport, library, or any area providing free WiFi. The hacker ensures that these places have multiple access points where the WiFi has similar names.
Step II
The hacker checks the available network and then sets up an account. They sets the account with a similar Service Set Identifier (SSID) and Basic Service Set Identifier (BSSID) as nearby networks. They may also use WiFi pineapple for a broader range and deceive the unaware user into connecting to it.
Step III
The fake access points are wireless cards. They are difficult to trace and may get shut off instantly. The attackers sometimes use WiFi pineapple’s help to create a more robust network. They move closer to the potential user, encouraging them to choose a stronger network over a weaker one.
Step IV
The attackers then ask the unwitting WiFi users to log into their fake server, prompting them to enter their user ID and password. The hackers have unauthorized access to the devices once the unaware user logs into their evil twin network.
The evil twin attacks can be dangerous as the hacker accesses the user’s bank details and social media accounts. More data theft happens if the user uses the same login credentials for other sites.
Effects of Evil Twin Attacks
The evil twin attacks not only individuals but also organizations significantly. It exploits users’ trust in public WiFi networks. The following are the effects of Evil twin attacks:
#1. Identity Theft

The evil twin attack can affect the identity of any individual as the hackers steal usernames, passwords, encrypted credentials like PayPal, emails, and other sensitive data from their systems.
#2. Unauthorized Data Access
Unauthorized data access can lead to fraudulent activities like breaches. The attacker can steal and alter the information and send messages or emails on behalf of the victim. He may transfer money, use services, or sell the account credentials.
#3. Financial Loss

If the hackers access the financial information in the system, they may do some unauthorized transactions, leading to significant economic losses.
#4. Malware Attack

Cyber attackers can also distribute malware to the system and steal data. The victims can unknowingly download the malicious virus while connecting to the network. These viruses can hamper the overall health of the system or device.
#5. Loss of Productivity
The evil twin attack can disrupt operations as the devices become offline for the attack investigation.
#6. Recovery Cost
Due to the evil twin attack, the organization suffers from financial loss, legal compensation, and investigations.
How to Detect Evil Twin Attack or Fake WiFi
Check for duplicate networks. If networks have identical names, an evil twin is likely mimicking a legitimate network.
If you find an Evil Twin network, always check its signal strength. The Evil Twin network will always have a stronger signal than the legitimate network. The attacker always increases the signal strength of the rogue access point so that the device automatically gets connected to a stronger signal.
Use network security software and network scanning applications. This software and applications detect and notify the user if they find any suspected WiFi threats. They also warn you if any malicious activity or network is detected.
How to Protect Your Gadget Against Evil Twin Attacks

- Connect to Familiar Networks: Always connect to known WiFi networks that are secured. Verify the network before connecting your device. Double-check the network name (SSID). Attackers usually use names similar to those of legitimate networks. Hence, verify the network’s name with the established public place staff. You can always avoid connecting to public WiFi, WiFi hotspots, and private networks.
- Use a VPN: A virtual private network (VPN) shields your data, activity, and traffic from hackers, even if you connect to an unstable, unsecured network. It creates encrypted tunnels and makes your data indecipherable from Evil Twin activities.
- Use Two-Factor Authentication: Two-factor authentication provides your online accounts with a double layer of protection. If the attacker tries to access your account with your credentials, he won’t be able to access it without the second authentication factor successfully.
- Update your Device’s Software: Always keep your device’s operating system and applications up-to-date. The software updates have security patches that protect your device from threats and attacks.
- Install Security Software: Install security software that notifies you about potential threats and suspicious WiFi networks.
- Use Cellular Data: Using cellular data is the safest method to prevent evil twin attacks when you are unsure of the security of a WiFi network.
- Disable Automatic WiFi Connection: Keep the auto-connection off your phone to prevent it from connecting to open WiFi networks. The auto connection tends to connect to a stronger signal, risking your device relating to an Evil Twin network.
- HTTPS Websites: Use https websites, which are safe and secure to browse. These websites protect and encrypt your daily activity, preventing hackers from doing malicious hacks.
Next, we will discuss what to do if you become a victim of an evil twin attack.
What to Do if You Fall Victim to an Evil Twin Attack
If an Evil Twin Attack breaches your data, you must take the following steps:
- The first step is to change the breached data’s username and password from the accounts.
- Monitor your financial activities. Check your bank and credit card statements.
- Check for viruses in your device by running a good antivirus scan.
- Reset all the network settings. Turn off all your auto-connect options on your device.
- If you suffered financial losses, complain to the FCC Consumer Complaint Center. Complaining to the bank authorities or credit card companies about breaching bank details. You can also complain to the customer service of the websites that suffered data breaches.
Other WiFi Security Risks
Some other WiFi security risks can be dangerous if we experience them. Let’s try to know them.
- Rogue Access Point: It also has unauthorized access to a network but is set up without the knowledge and approval of the network administration. The purpose of the rogue access point is to intercept data traffic, launch a denial-of-service attack, or gain unauthorized access. The significant difference between the Evil Twin attack and the rogue access point is the intent and execution. The employees can create the rogue access point unintentionally, but the intention of an Evil Twin attack is data theft.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: In this attack, the attacker relays and alters the communication between the two parties. Here, the ignorant parties believe they have direct contact. This attack can lead to data theft, modification, or injection of malicious content.
- Weak Passwords: Weak passwords can lead to brute force attacks, the primary reason for cyber-attacks and data thefts.
- Unencrypted Traffic: If the network is not encrypted, the data is visible when the traffic gets transferred to the other network. It can lead to the stealing of data and especially financial loss.
- Data Sniffing: This attack allows the attackers to capture data while transferring over a network.
Examples of an Evil Twin Attack
Let’s take an example of an Evil Twin Attack. Let us consider a person in a public place, say at a hotel, studying at a library, waiting for a flight at the airport, or in a cafe. He checks the available networks and finds two WiFi networks with a similar name. One of the networks out of the two is an Evil Twin network trying to deceive the user.
The unaware user connects with the Evil Twin network due to its strong network signal. The hacker gets unauthorized access to his device once the unaware user connects to the rogue network.
The attacker can now access all the victim’s activities, username and password, bank details, unencrypted credentials, and sensitive data.
Best Practices for WiFi Security

Here are some best practices to keep your WiFi network secure. Some of these practices are similar to the Evil twin attack prevention methods.
✅ Use a Firewall: Firewalls block incoming unauthorized traffic and protect your device from cyber-attacks.
✅ Use MAC Filtering: MAC filtering allows devices with MAC addresses to connect to your network. This filtering prevents unauthorized access and malicious practices.
✅ Use Strong Passwords: Strong passwords with upper- and lower-case letters, digits, and special characters are also one of the best practices for WiFi security.
✅ Disable SSID Broadcast: When we turn off the SSID broadcast, it prevents other devices from detecting your SSID or WiFi network when they try to view nearby wireless devices.
✅ Disable WPS: When we disable WPS, we prevent our device from unauthorized access and enhance its network security.
✅ Disable Remote Management: Turning off the router’s remote management prevents attackers from accessing the router’s settings.
Final Words
By being mindful and taking reasonable precautions, the user can reduce the probability of getting victimized by the Evil Twin attack and prevent themselves from other cyber attacks.
Next, check out how to prevent attack vectors on your network.

