IMAP is the standard email protocol that is used for retrieving emails. This special layer allows computers and servers to share messages with each other.
You must have been accessing and using email for a long time, whether through a PC, laptop, or smartphone.
But have you ever wondered what allows you to easily access those emails and use them as if they are stored locally on your PC or smartphone?
It is IMAP that determines how the server or computer will work on an email. It makes accessing emails easy for users.
Let’s understand what IMAP is, how it works, its benefits, and other vital details.
What Is IMAP?
Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) is a popular layer protocol through which email clients receive emails from a mail server over the IP/TCP connection. It was developed by Mark Crispin in 1986, making it easier for users to access mailboxes from a remote location as if it is present locally.
It is one of the most used email protocols in the industry that allows users to access emails seamlessly. Most servers and email clients, including Google, Outlook, and Mozilla Thunderbird, support IMAP.
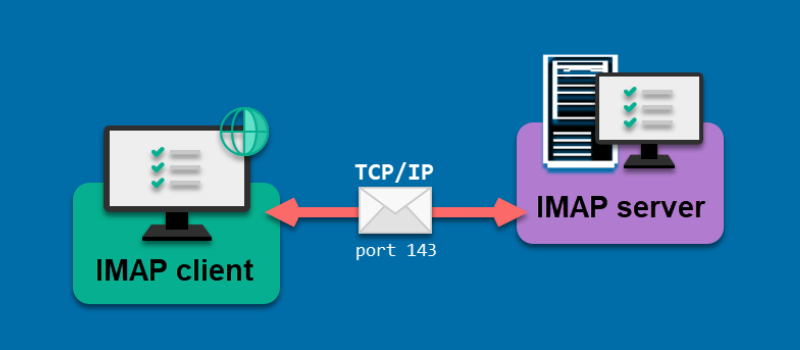
The feature distinguishing IMAP from others is its ability to allow users to access all their email from any device they want. Basically, it acts as a bridge or intermediary between email client and server so you can readily access them rather than having to download them.
In IMAP, the server stores all your email that has already been delivered and allows you to read it anytime by using the server as a medium. Since it is stored centrally, any changes to a specific email are dynamically updated. And you will see the change when you access the email from another device.
However, you will need an internet connection to access and see those changes in the email. Besides reading, these layers will also enable you to organize your folders, save messages as a draft, and flag messages on the server.
What’s more?
You can use multiple email applications to access all your emails, and IMAP will enable those apps to stay synced with the email and show the email’s current status. IMAP largely depends upon the TCP/IP transport layer because it helps read and modify email over the internet.
When the TCP connection is made between the server and the client, IMAP utilizes port 143 as a default. However, this is not the only port IMAP utilizes, as it also listens to Port 993 when the clients want to connect to the server securely via SSL/TLS connection.
How Does IMAP Work?
IMAP is an incoming email protocol that acts as an intermediate layer between the email server and the client. The working of the IMAP is quite simple and seamless, and it only needs a TCP/IP transport layer to get the job done.
When the connection is established between the server and the client, as a user, you just read an email from the server and do not download it. While accessing emails, you might feel the emails are locally available, but in reality, they are stored in the email server.
Due to this, IMAP allows you to access emails from any device and any location you are residing. Whether it is a smartphone, PC, laptop, tablet, or anything else, it won’t matter as you will read the server’s emails through IMAP.
Functioning of IMAP
For your understanding, the following steps will give you a detailed view of each process in the functioning of IMAP:
- As a user, the first step you take is to sign into your email client’s account, and while logging in, the client reaches the email server through IMAP. IMAP works with most email clients, such as Gmail, Outlook, Thunderbird, etc
- Next, IMAP uses Port 143 or 993 to establish the connection between the email server and the client. IMAP, while working over Secure Socket Layer (SSL), it is automatically assigned to Port 993. Over TCP/IP, it’s assigned to port 143.
- Once logged into the email account, the client shows you a header of all the recent incoming emails. By scrolling and clicking the next page, you can access the subject header of all the emails.
- When you want to read a particular email, IMAP downloads that particular email and helps you see all the details under the header. However, only the message is automatically downloaded and not the attachment.
- Email clients mostly utilize IMAP as an intermediate layer because it allows quick email access. Most importantly, it is quite secure, so there is no chance of unauthorized access. There are many email retrieving protocols like POP and SMTP, but IMAP offers the smoothest and quickest functioning.
- Once you read the email from the email server, it stays in the server unless you make any modifications. All the modifications you make in your mailbox are dynamically updated, and you will see the same modification while accessing from different devices. IMAP doesn’t delete the accessed emails automatically unless you delete them.
Next, we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of IMAP.
Advantages and Disadvantages of IMAP
Every email retrieval protocol has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s discuss those associated with IMAP.
Advantages of IMAP
- With IMAP, emails are only auto-downloaded when you click on them; hence, it offers seamless and quick access to emails through the client without needing to download them in the first place.

- You can access your email through an email client from anywhere in the world, and that too from any device you have, whether it is a PC, tablet, or smartphone. Emails are always synced to the server, so it is readily available.
- Besides keeping incoming messages, IMAP stores all your emails, whether received or sent, in a remote IMAP server. Thus, you can access all the emails anytime, and it will feel that they are stored on your device’s local storage.
- IMAP enables emails to be accessed offline. The attachments can also be accessed after you have downloaded them.
- You have the option to organize your emails on the server in various folders and sub-folders. You can even flag emails that are important to you. In addition, you can read, sort, search, and organize your emails with ease.
- IMAP supports IDLE extension, where the email client shows which email is unread or read in the inbox.
- It is a simple, fast, and easy-to-utilize email retrieving protocol that you won’t easily find in other protocols. The process is so streamlined that it helps you quickly access emails over any internet connection.
Because of these benefits, IMAP has become quite popular in the industry and among users leveraging leading email clients.
Disadvantages of IMAP
Although IMAP offers many advantages, it has some disadvantages as well. Here is the list:
- You would always need an internet connection to easily read, download the attachment, and send and reply to emails through your client. You can only go through certain emails that you have already read when you don’t have internet access.

- You won’t be able to access all the received emails when you are offline. Moreover, if there is a server issue or internet outage, you won’t have access to the received or sent emails.
- IMAP requires a lot of server storage because all the received and sent emails are stored on the server. For limited server storage, you will have to delete old emails to accommodate new ones.
- If you receive a lot of emails daily, then you will have to look to buy more server space.
- IMAP’s authentication mechanism can be bypassed by hackers who can use a protocol analyzer and retrieve usernames and passwords easily as they are transferred in simple text.
Security Concerns in IMAP

IMAP may be growing day by day due to its perks and compatibility with multiple devices, but it has certain security concerns, such as:
- The server where all emails are stored can cause serious issues if compromised. If the email provider’s server somehow malfunctions or shuts down inappropriately, then you might not be able to access any of your emails.
Moreover, if it is compromised, hackers will access all your important documents and others’ personal details.
- IMAP transmits username and password from the client’s end to the server without encryption. The login details are transmitted in the form of plain text. This way, hackers can easily use an analyzer and steal login details from clients.
However, when IMAP is integrated with TLS protocol, the login details can be encrypted while communicating.
- The lack of inherent compatibility with MFA or multi-factor authentication is one of the major problems associated with IMAP. Because of this, hackers can easily utilize password-spraying techniques to illegally log into different email accounts.
It is a huge concern for many organizations using email clients with authentication facilities because it puts a lot of information vulnerable. Therefore, many organizations prefer to avoid using IMAP.
IMAP vs. POP3
POP3 and IMAP are two of the widely used email protocols. Let’s discuss some differences between them.
| IMAP | POP3 |
| Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) is an advanced protocol that allows you to view all the folders on a server. | Post Office Protocol (POP3) is a straightforward protocol that allows downloading messages from the inbox to the local computer. |
| Here, users access their emails from the device they want. | Here, emails can be viewed or accessed from the device where they are downloaded. |
| IMAP acts as the intermediary between the client and the server. Hence, the server stores each email. | Emails, once downloaded, will be deleted from the server without any configuration. |
| You can’t access emails offline. | You can access emails offline but on the same device. |
| Until a user clicks on the bodies of the emails, it will not download; sender names and subject lines populate in the email client quickly. | By default, emails are downloaded; hence, they take longer to load. |
| Since emails are not deleted automatically from the server, IMAP needs more space to store them. | Since emails are deleted automatically from the server, POP3 saves email storage space. |
FAQs
Answer: IMAP is getting outdated gradually as Microsoft has stopped supporting username and password authentication for IMAP. Along with Microsoft, many email clients also have stopped supporting this protocol. However, there are some email clients that still support this email retrieving protocol and continue to bring improvement.
Answer: IMAP could be safer because all the emails are stored on the server. Even if your phone is lost or some malfunction happens on the email client’s end, all your emails are safe with the server. However, with POP3, all the emails are downloaded and stored on the device, and it could be a serious problem if the device gets stolen or lost.
Answer: You won’t lose emails if you import and export in Outlook while changing from POP to IMAP. You just need to create a new IMAP account in your email client and simply export the message from POP to IMAP.
Final Words
This article will give you an idea of IMAP and how it works. This email retrieval protocol makes accessing emails quite a straightforward task. It offers many perks and features that make IMAP an excellent choice for many email clients.
Next, check out apps to clean up your email inbox.

