Cybercriminal activities are making headlines today. It has become easier for hackers to access business systems and email accounts in this technological age.
According to a recent IRONSCALES survey, 80% of organizations worldwide experienced increased email phishing attacks in March 2020, and around 94% of malware is delivered through emails. Another statistic suggests that around 1.2% of all emails are malicious, accounting for around 3.4 billion phishing emails a day.
These attacks compromise email security, accounts, communications, and sensitive data via unauthorized access, resulting in tremendous business loss, reputation, and revenue.
Hence, organizations must enforce robust email security practices and establish data loss prevention solutions and policies that protect them against cybersecurity attacks like spam, malware, and phishing.
And one of the essential components of email security is PGP Encryption.
PGP, or Pretty Good Privacy, is a security system that offers your email data security and protection from prying eyes. In this blog, we’ll learn more about PGP encryption, how it works, its benefits, use cases, and more.
What is PGP Encryption?
PGP is an encryption system that encrypts and decrypts emails and authenticates email messages via file encryption and digital signatures.
Cybercriminals often target emails to forge data and messages using the user’s name or identity. PGP encryption solves this issue and enhances email security by encrypting email data and making communication more private.
It scrambles the data to make it unreadable to those without the means to decode it. This encryption system was first developed and designed in 1991 by Pual Zimmerman. PGP was the first free and publicly available public-key cryptography software, initially used by individuals for communicating on bulletin board system computer servers.
Later, the system was supported and standardized for other applications, like email.
PGP uses public-key and symmetric encryption, allowing users to send and receive encrypted messages without exchanging private encryption keys. Thus, in simple terms, PGP provides cryptographic authentication and data privacy for online communication.
PGP encryption lets you encrypt and decrypt:
✅ Text messages
✅ Files
✅ Disk partitions
✅ Computer files
Thus, PGP encryption provides a seamless, cost-effective, and secure solution to improve email messages and digital communication security.
How Does PGP Encryption Work?

PGP encryption works by encrypting or scrambling data or a message that makes it unreadable and difficult for others to decode the message—ensuring high confidential data security.
On a technical level, it uses a combination of data compression, cryptography, and hashing techniques. Thus, it uses private, public, and session keys to protect data.
PGP encryption is similar to other popular data encryption techniques, like
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption, which secures websites
- Kubernetes, which is used to authenticate network users
- Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), which protects the data in motion
PGP encryption uses the public key system, where each user consists of a unique encryption key that’s known publicly and a private key that is private to them.
Thus, when a user intends to send a private message or an email, the receiver generates a private and a public key—keeping the private key to themselves and sending the public key to the sender.
The sender encrypts the message with the help of the receiver’s public key (an encryption key known to every user) and sends the private encrypted message to the receiver. Once the receiver receives the encrypted message or the email, they decrypt it using the private key. This process ensures that the email or message gets to where it’s intended to be sent and that only the receiver can decrypt it.
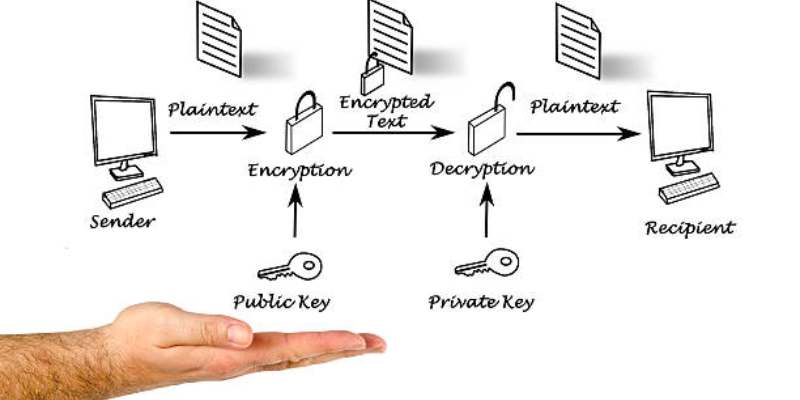
At the technological level, PGP encryption works by following the three steps:
- Step 1: PGP generates a huge and highly complex single-use public encryption algorithm that’s difficult to guess, which becomes the random session key.
- Step 2: PGP then encrypts this random session key using the recipient’s public key, protecting the message in transit. The recipient can share this public key with any user to receive messages.
- Step 3: The sender sends the PGP encrypted message session key to the recipient, allowing the recipient to decrypt the message using the private key.
While encrypting the entire message can take a lot of time, PGP encrypts it with the help of a faster algorithm. It compresses the plaintext data, saving disk space and transmission time and reinforcing cryptographic security.
The public key encrypts the shorter version of the encrypted message, which is sent to the receiver, and the receiver uses the private key to unlock the shorter key and then decrypt the entire message.
The PGP encryption uses efficient algorithms that help create a mathematical summary called hash to send digital signatures. The hash code can be digital data like a username encrypted by the email sender’s private key. The recipient decrypts the hash using the sender’s public key, and if it matches, it confirms that the message is received securely.
Uses of PGP Encryption
PGP encryption is widely used where people are required to confidentially send data and messages using a combination of private and public keys to ensure technological privacy.
The most common and primary uses of PGP are:
- Sending and receiving encrypted emails
- Verifying the message sender’s identity
- Encrypting files stored in the cloud or on your devices
Let’s look at each one of these uses briefly:
#1. Encrypting Emails

Emails have become a common and crucial mode of communication for exchanging personal data and business communication. However, it comes with many risks related to malware, data breaches, and cybersecurity attacks.
Cybercriminals can easily intercept and compromise email messages and accounts and gain unauthorized access without a robust encryption and security system.
While PGP encryption was initially used by individuals willing to share confidential information, like journalists and activists, it has gained significant popularity in encrypting emails.
PGP encryption eliminates unauthorized access issues using its secure data and information exchange process.
#2. Encrypting Files

PGP encryption uses one of the most secure algorithms—the RSA algorithm that’s deemed unbreakable, making it ideal for encrypting files. As a result, PGP is highly effective in encrypting files, especially when used with a response solution and threat detection.
You can use PGP encryption to encrypt and secure files stored on your computer, cloud, or storage devices, like an external hard drive or a flash drive.
#3. Digital Signature Verification

Email verification is another crucial use of PGP encryption, enabling individuals to ensure the file’s and document’s authenticity and verify the sender’s identity.
For instance, if the email receiver has doubts or isn’t sure about the sender’s identity sending the email, using a digital signature in conjunction with PGP encryption is highly beneficial in verifying the sender’s identity.
Digital signatures use an algorithm combining the sender’s key with the message they want to send. This process generates another algorithm called the ‘hash function’ that converts the email message into a block of fixed-size data, which is then encrypted using the sender’s private key.
The recipient can then decrypt this message using the sender’s public key. Even if one of the message’s characters has been changed during the transit, the recipient can determine it. It indicates that the sender isn’t someone they’re claiming to be (trying to fake the digital signature) or the message has been tampered with or altered.
How to Set up PGP Encryption?
Setting up and using PGP encryption includes downloading an add-on for your email client or program and following the installation instructions.
Add-ons are available for email clients, including Outlook, Thunderbird, Apple Mail, and more. In addition, several online email systems, like ProtonMail, also consist of PGP by default. Hence, in such cases, you need not download an additional add-on.
Several large-scale software solutions, like Symantec, offer PGP-based products, including Symantec Endpoint Encryption for full-disk encryption on mobile devices, desktops, and removable storage and Symantec File Share Encryption to encrypt files across the network.
Typically, the first step to enable PGP encryption is downloading PGP encryption software that automates the encryption and decryption.
Here are a few tips for selecting an appropriate PGP software from multiple options that best meet your needs.
- Security should be the primary factor when looking for suitable PGP software. While PGP is unbreakable, spotting vulnerabilities that can compromise data isn’t possible; hence, checking for reported vulnerabilities in the PGP software you consider is essential to ensure maximum security.
- Next, you must choose a PGP software that meets your specific business needs. For instance, you might not want to encrypt every email you send, and using an add-on for your everyday email communication might be overkill and unnecessary. Hence, you must choose PGP software only to send important emails.
- Choosing a PGP software offering dedicated customer support through a reliable support team or a user community is crucial to avoid frustrations or confusion when using and navigating the system. In addition, this allows you to seek help whenever necessary.
Depending on your needs, purpose, and reasons behind using PGP encryption, you can follow and implement different approaches for setting it up.
Here are a few critical approaches or solutions to implementing PGP encryption on your business or home networks:
- Outlook with Gpg4o is a popular PGP solution for Windows users that seamlessly integrates with Outlook 2010-2016 and offers an easy and user-friendly solution to handle emails.
- ProtonMail uses PGP encryption for messages automatically for messages transferred between two users and uses a web portal, making it easily separable from your everyday inbox. Hence, it removes the complexity of using and setting up PGP encryption.
- Enigmail integrates with one of the most popular email clients, Thunderbird, a platform-independent, free, and open-source add-on. In addition, it comes with a dedicated development team that’s quick to respond to instances like malware.
- GPGTools is a software suite that integrates with Apple Mail and is one of the standard PGP encryption implementations for Mac users, offering data encryption for all the areas of your Mac system.
- FairEmail is a free, standalone email application that extends PGP encryption to Android phones. It doesn’t offer PGP encryption by default and allows you to encrypt messages and choose what to encrypt.
Once you download suitable software, you can generate private and public keys directly from the platform/software. This will give your email client an option to encrypt the email message, allowing you to communicate securely with PGP.
Challenges of Implementing PGP Encryption
Despite offering several advantages and being an affordable encryption option, PGP encryption has many drawbacks and implementation challenges, as mentioned below.
#1. Complexity
PGP encryption is pretty complex and takes effort and time to exchange complicated messages among users and understand the processes, especially for novice users.
Furthermore, since PGP encryption comes with conceptual complexity, it requires extensive employee training to understand key PGP processes and concepts. This results in a usability issue, making PGP implementation difficult at both GUI and the command line.
#2. Key Management
Managing PGP keys can be a challenge. You must understand efficient key management to prevent incorrectly using, corrupting, or losing PGP keys, failure to which can put other users and vendors at risk.
#3. Infrastructure
Decentralized infrastructure that lacks a central authority controlling the distribution of public keys is another critical challenge with PGP encryption.
Using a web of trust can be a huge problem with fewer participants in the larger general population as there isn’t a single trusted source of information about public keys.
#4. Compatibility
PGP encryption also comes with compatibility issues as it’s not supported universally by all email clients and platforms. This can create difficulty in using PGP encryption to communicate with those without PGP encryption or other encryption methods.
#5. Key Revocation
If you lose your PGP key or it gets stolen, revoking it or generating a new one can be challenging. This makes it easier to compromise the information, leaving it vulnerable to interception.
#6. Trust
PGP encryption heavily relies on the involved party’s trustworthiness. If any of the senders or receiver’s private keys are misused or compromised, the entire communication and its data are at risk.
Final Words
Monitoring third-party attacks and system vulnerabilities that threaten your business reputation and data security is crucial.
PGP encryption is a powerful tool to improve the integrity, confidentiality, and authenticity of your email communications, files, and confidential data. However, at the same time, online email security doesn’t start and end with PGP encryption.
Hence, you must analyze your business’s security needs and opt for comprehensive business security tools that protect against cybersecurity attacks, like malware, phishing, DDoS, and other security attacks.
Next, check out how much is your personal information worth on the dark web.


