Windows Command Prompt can perform many unique tasks that usually can’t be done by other Windows components. Best of all, it works even when other Windows components break, making it the best tool for system admins to master.
As a system administrator, the Windows command prompt can help you get more information about computers and run automatic commands on multiple computers at once to complete tasks remotely. Whether you want complete information about connected networks, fix file errors, get info about hardware components, or manage volume drives, you can do it all via command prompt.
Windows Command Prompt Commands You Should be Aware of
If you are new to using the command prompt as a system admin, then I can give you a boost to get started. Although there are hundreds of commands, in this post, I will list some of the most useful ones that system admins commonly use.
Let’s see some Windows command prompt commands that will help you as a system admin.
ipconfig/all
Whether you need to fix connection errors or create a remote connection with other PCs, ipconfig/all command is your best friend. This command will show all the network configuration values in one place. This includes hostname, IP address, default gateway, subnet mask, network features, and much more.

Microsoft also has a handy guide on the ipconfig/all command on its website. You can check it out here.
Tracert
If the computers you are administrating are part of a large network and connected via multiple routers or bridges, the tracert command can help find network issues by tracing the route a packet takes. This command can show each host the packets routes through while reaching a specific host. Using this information, you can track the cause of the problem where the packet is getting lost.

It also tells the time it takes to reach each host, so you can also track network performance issues.
DriverQuery
The command driverquery shows the complete list of installed drivers in your PC, along with the history of when they were installed. Although the Windows Device Manager is a better tool to fix driver issues, this command can help when you need to track driver installation history.

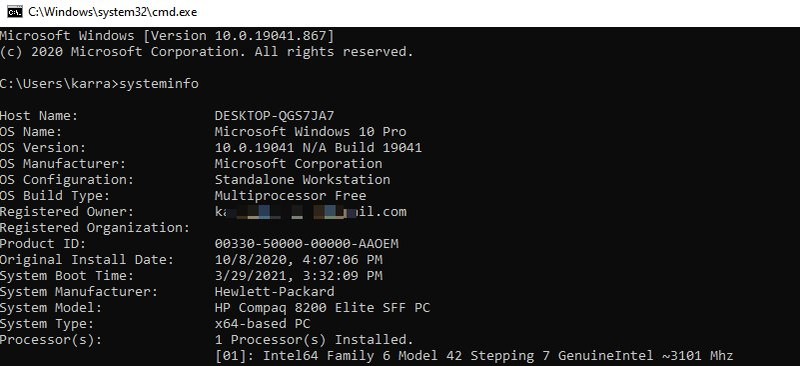
SystemInfo
With systeminfo command, you can view detailed information about your PC and the OS, such as system owner, PC model, boot time, network name, system type, and much more. It also shows basic information about hardware, including processor, RAM, and disk space.
Powercfg
The powercfg command is used to manage the power options of Windows. Unlike the regular power options settings of Windows, powercfg lets you run commands that are impossible to do from power settings, like import/export settings or track wake times.
SFC/scannow
SFC (System File Checker) is the command used to check all the system files and look for errors. Once found, the command will automatically replace the file with a new one from the cache. Although it has multiple parameters, the most common one is sfc/scannow that simply runs the scan on all the system files.

Chkdsk
This command is used to scan the hard drive for logical or physical errors and automatically fix them. However, you need to use the right parameter to fix the errors. For most users, the command chkdsk/r should be enough to find and fix file system errors and bad sectors automatically.
Also Read: Repair Tools to Solve Windows 10 Problems Automatically

Netstat
A powerful network troubleshooting command that shows both incoming and outgoing connections to your PC, along with the protocol type. Not only that, but you can also use netstat command to do a bunch of other things using parameters. You can see the routing table, the number of bytes and packets sent/received, process ID (PID), program name that established the connection, and many more.

Tasklist
A simple command to see the currently running processes on a PC, similar to the processes tab in the task manager of Windows. However, tasklist command is more useful for seeing processes of another PC remotely. However, keep in mind that it doesn’t show memory usage in real-time, unlike the task manager.
GetMac
If you need to see the MAC address of a PC or multiple PCs connected over a network, then getmac is the right command. Using without parameters, it will show the MAC address of the current device. Although, you can use parameters to view the MAC addresses of PCs over a network.

Shutdown/s
The shutdown command has many parameters to control the shutdown and restart of a PC or multiple PCs remotely. The command shutdown/s will shut down the current PC after a delay. You can also use parameters like /r or /h to restart the specified PC or put it in a hibernate state.
Definitely, a must-know command to quickly shut down multiple PCs you are managing.
Assoc
You can use this command to view and manage file associations of a PC. The assoc command will list all the file extensions along with the programs associated with them. You can add the extension next to the assoc command to see the program associated with that extension; for example, assoc .mp3 will show the program that runs mp3 files on the PC.

You can also use parameters to change file associations on the PCs remotely.
Robocopy
It’s similar to the copy/paste feature of Windows, but it’s extremely customizable using parameters. The basic robocopy <source> <destination> <file> command will copy/paste the file to the specified destination. You can add parameters like /nocopy to remove associated information or /s to exclude empty subdirectories.

This command has dozens of parameters that can give full control over moving data, perfect for managing data between multiple PCs.
Format
If you need to format the disk without access to the formatting feature of Windows, then format is a powerful command to do it. You need to provide the volume label, and the command will delete all the data on that volume. You can also configure file system type, change volume label, change allocation unit size, create compressed volume, and much more using parameters.
Hostname
You need to know the hostname of a computer to create a remote connection, and hostname command can easily tell you the name of any PC. Just type hostname, and the command prompt will immediately tell you the hostname of the PC. It’s a simple command that doesn’t even have parameters, but it’s extremely useful when you need to create remote connections.

Ending Thoughts
These were command prompt commands that I believe will immensely help with a system administrator’s day-to-day tasks. If you are interested in learning more commands, you can check the Windows commands list by Microsoft. You can click on any of the commands to learn what it does and see its parameters.

