IGMP snooping is a critical tool for efficient network management and a must-have for any network administrator looking to enhance their network’s performance.
You’ve heard of IGMP snooping, right?
If not, don’t worry because I’m about to blow your mind!
What is IGMP snooping?
It’s a feature on network switches that helps optimize and control the flow of multicast traffic on a network.
Essentially, what it does is that it allows the switch to listen to the conversations happening between hosts and multicast routers through the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) messages. This snooping helps optimize the delivery of multicast traffic by selectively forwarding packets to only those ports where receivers are interested in the multicast stream.
Now, when a multicast source sends a packet to a multicast group address, the router forwards it to all the ports in the same VLAN. However, that may not be ideal since not all hosts in the network may be interested in receiving the multicast traffic. This can lead to a wastage of network bandwidth and unnecessary processing overhead on the hosts.
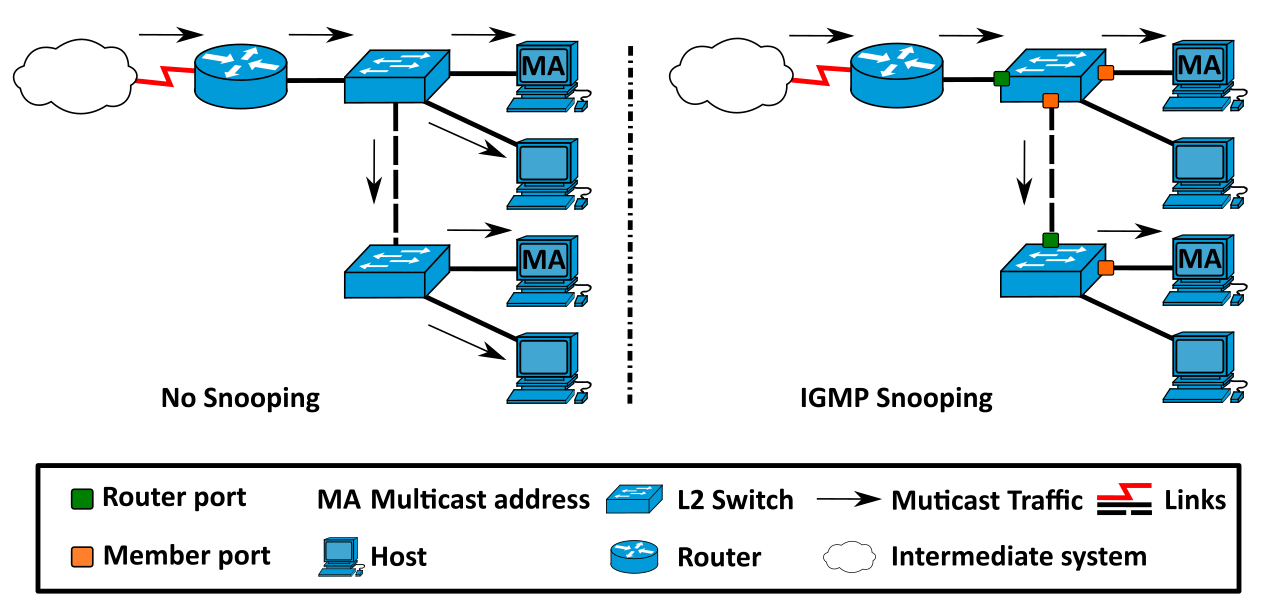
To address this issue, IGMP snooping comes into play. By monitoring the IGMP messages exchanged between hosts and routers, the switch can learn which ports are interested in receiving the multicast traffic and accordingly forward the traffic only to those ports. This not only improves network efficiency but also reduces network congestion to a great extent.
In order to maintain this selective forwarding, the switch maintains a table of multicast group memberships that it learns from the IGMP messages sent by hosts and routers. The switch then uses this table to determine which ports should receive the multicast traffic.
How does IGMP snooping work?
When a host wants to join a multicast group, it sends an IGMP membership report to the network. The IGMP snooping feature on the switch intercepts this report and creates a multicast forwarding table. This table contains the MAC addresses of the hosts that are members of a particular multicast group and the ports on which they are connected to the switch.
The switch uses this table to forward multicast traffic only to the ports where interested hosts are connected. This selective forwarding helps to reduce network congestion and improve network efficiency. It’s like a traffic cop for your network!
If a host leaves a multicast group, it sends an IGMP to leave a message to the network. The switch intercepts this message and removes the host’s entry from the multicast forwarding table.
IGMP snooping also provides additional features such as multicast filtering and VLAN support. Multicast filtering allows the switch to filter out unnecessary multicast traffic, as explained above, while VLAN support allows different multicast groups to be segregated into different VLANs.
It’s like a VIP section for your network traffic!
Benefits of IGMP Snooping

Reduced Network Congestion
Imagine a network where multicast traffic is being sent to all ports, even if not all hosts are interested in receiving it. This would lead to a lot of unnecessary traffic, hogging the network bandwidth and causing congestion.
However, with IGMP snooping, the switch can selectively forward multicast traffic only to those ports where receivers are interested in the multicast stream. This helps reduce network congestion by minimizing unnecessary traffic and conserving network bandwidth.
Improved Network Efficiency
When multicast traffic is being forwarded to all ports, it can cause a lot of processing overhead on the hosts and network devices, which can lead to latency and slower performance.
However, with IGMP snooping, the switch forwards multicast traffic only to the required ports, which reduces the processing overhead and improves network efficiency.
Better Security
Multicast traffic may contain sensitive data that should not be accessed by unauthorized users. IGMP snooping ensures that multicast traffic is only forwarded to specific ports, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data and enhancing security.
Simplified Network Management
The multicast group membership table is automatically learned and updated by the switch with IGMP snooping. This reduces the complexity of network management, saving time and effort for network administrators.
Better Quality of Service
IGMP snooping allows network administrators to prioritize multicast traffic and allocate network resources accordingly. This ensures that high-priority traffic, such as real-time video and audio streams, receives the necessary network resources and delivers a better user experience.
By optimizing the network resources, IGMP snooping can provide a better quality of service for multicast traffic.
What is Network Switch?
Have you ever wondered what a network switch is?
Well, wonder no more!
A network switch is a device that connects devices on a local area network (LAN) & forwards data packets between them.
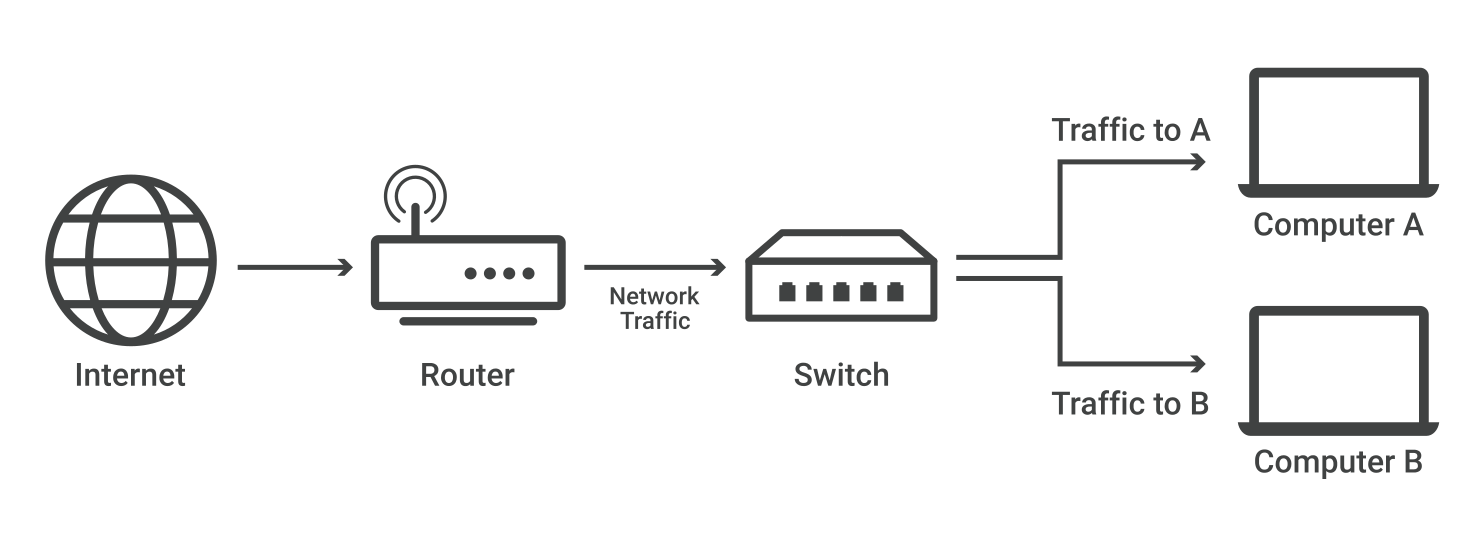
Unlike a hub that simply broadcasts data to all connected devices, a switch filters and forwards data based on the MAC addresses of the connected devices. This filtering capability helps improve network security by preventing unauthorized access to data and reducing the likelihood of network collisions.
Network switches act as a central hub for devices such as computers, printers, servers, and other network-enabled devices which enables efficient data transfer by creating a dedicated communication link between the sender and receiver of the data. This minimizes network congestion and ensures high-speed data transfer.
But wait, there’s more!
Network switches often provide additional features such as Quality of Service (QoS) prioritization, VLAN support, and Power over Ethernet (PoE) to power devices such as wireless access points & IP phones.
Network switches are essential components of modern LANs, which provide reliable and efficient communication between network devices. So, whether you’re connecting to the internet or sharing files with your colleagues, you can thank your trusty network switch for making it all possible!
How to configure IGMP snooping?
Are you ready to learn how to configure IGMP snooping on your network switch?
Hold on tight because this is where things get exciting!😃
Prerequisites
- A switch that supports IGMP snooping.
- Knowledge of your network’s VLAN configuration and multicast traffic requirements.
#1. Enable IGMP snooping
The first step is to enable the IGMP snooping feature on your switch.
This can usually be done through the switch’s web-based management interface or command line interface (CLI).
The exact process may vary depending on the switch model and vendor. But in general, you can follow these steps.
- Log in to the switch’s management interface.
- Navigate to the IGMP Snooping settings page.
- Enable the IGMP snooping feature.
- Save and apply the changes.
Just remember, different switches may have different ways of enabling this feature. so make sure to read the documentation.
#2. Configure IGMP snooping parameters
Next up, you may need to configure some IGMP snooping parameters like the IGMP version, multicast router port, and Querier mode.
What are these, you ask?
Well, the IGMP version determines which version of IGMP protocol is used on the network, the multicast router port is the port that connects to the multicast router, and Querier mode is used to elect a multicast Querier on the network.
#3. Configure multicast VLANs
If you’re using VLANs on your network, you might want to create some multicast VLANs to segregate multicast traffic into different VLANs.
- Identify the multicast traffic requirements of your network environment.
- Configure the VLANs and assign multicast traffic to the appropriate VLANs.
- Ensure that the switch is configured to forward multicast traffic correctly between VLANs.
This can help improve network performance and reduce congestion.
Who doesn’t want their network to be faster and less congested, right?
#4. Verify IGMP snooping configuration
Now that you’ve enabled IGMP snooping and configured all the necessary parameters, it’s time to verify that everything is working correctly.
You can do this by checking the multicast forwarding table to ensure that it contains the correct information about multicast groups and their associated ports.
This is like checking your network’s pulse to make sure everything is running smoothly.
If you need more help in IGMP snooping configuration using CLI, Feel free to watch this video.
Troubleshooting common Issues
Incorrect VLAN Configuration
Be sure to allocate all ports necessitating multicast traffic to the appropriate VLAN and check that the VLAN’s multicast settings are properly arranged.
Multicast Group Membership
Verify that multicast traffic is being directed to the precise ports by ensuring that the multicast group membership is properly configured on the switch and that the hosts are competently transmitting IGMP join messages.
IGMP Snooping Table
If the IGMP snooping table is lacking information, confirm that the IGMP querier is performing efficiently and that IGMP messages are not being blocked by any firewall or security settings.
Reset Configuration
If all else fails, you may consider resetting the switch to its default settings and then reconstructing IGMP snooping from scratch.
By sticking to these steps and utilizing these troubleshooting techniques, you’ll be well-equipped to both configure & resolve issues with IGMP snooping on your network.
Remember to approach each issue systematically, and don’t hesitate to seek guidance from a professional if the need arises.
Final Thoughts✍️
As the field of networking continuously evolves and expands, it’s becoming increasingly vital to effectively manage multicast traffic on local area networks.
IGMP snooping is a technology that enables switches to selectively forward multicast traffic only to the ports that require it, thereby avoiding a flood of traffic to all ports.
The end result?
Enhanced network performance, less congestion, and a critical tool for network administrators.
With the appropriate knowledge and tools, Anyone can effectively establish and maintain IGMP snooping on their networks.
I hope you find this article helpful in learning about IGMP snooping and how to configure it.
You may also be interested in learning about the best deep packet inspection tools to analyze network traffic.


