As the world becomes more connected, it’s essential to protect ourselves from possible cyber threats. We all use digital technologies at work, in our personal lives, and to move around us. With improved protection measures, we can play an active role in creating a safer online environment for everyone.
Cybersecurity and its Impact
Cybersecurity is an integral part of today’s digital world, where it secures crucial information as well as vital infrastructures from cyber-attacks. Cyber threats may be diversified – starting from malicious attempts to gain unauthorized access to a system or network through the disruption of activities or services that stop normal business processing.
Companies must have some active defense mechanisms such as training for their employees, regularly updating security policies and procedures, upgrading technology for up-to-date protection solutions, and regular audits/assessments of the system’s security status along with response/mitigation plans like seeking assistance from bug bounty platforms when needed.

Such professional cybersecurity experts are trained to recognize and cater to those risks associated with potential attacks – ensuring the safety and continuation of just about any organization’s data assets against a wide variety of possible assaults by hackers every day.
That is to say, these measures safeguard businesses, be it personnel-wise or technologically, to prevent any form of malicious activity to stay safe.
Cyberattacks cause a lot of harm both to individuals and their organizations. Cyberattacks may lead to identity theft, monetary loss, and even physical harm to an individual user.
To the organizations, too, they mean everything from data breaches to a possible dent in the reputation after that, losses. The critical infrastructure is not spared either because if successfully attacked, it becomes disrupted, just like crashing power grids and transportation systems.
Future Trends of Cybersecurity
With a rapidly changing technology landscape, organizations need to be always on their toes in protecting themselves from new emerging threats.
Organizations can feel safe that as long as they develop a comprehensive strategy that gives not only defense but also an offense against potential attack. Only then, their investments in cutting-edge technologies are one step ahead of malicious actors leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning for new threats like deep fakes.

As technology advancements continue, cybercrime is increasingly becoming an imminent threat.
Organizations must take significant steps to guarantee their data and systems are secure to safeguard against the projected $10.5 trillion loss due to malicious activity by 2025. Considering such a considerable impact, businesses cannot afford not to prioritize cybersecurity measures for risk mitigation and prevention.
Apart from making the employees aware of phishing as well as password practicing along with a contingency plan to counteract quickly when an incident takes place, security strategies involve encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. As technology is fast changing and evolving, it becomes an absolute necessity that organizations are always in touch with effective cybersecurity solutions so that digital security is maintained now and even in the long run.
Users can keep themselves protected against cyberattacks by using strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, not sharing sensitive information online, being suspicious of phishing emails and other social engineering attacks, updating software regularly, and having a reliable security solution.
The following are some Statistics and Data to showcase the cyberattacks and associated cost and impact:
Surge in Data Breaches
Data breaches in the United States surged to 1802 cases in 2022
As per Statista, in 2022, in the United States alone, 1802 data breaching incidents occurred and affected 422 million individuals. All these breaches involve unauthorized access to sensitive data by a malicious actor.
Healthcare was found most vulnerable, with cases going up over time, while financial services suffered a near doubling between 2020-2022, and manufacturing saw over thrice that rate of increase within those two years.
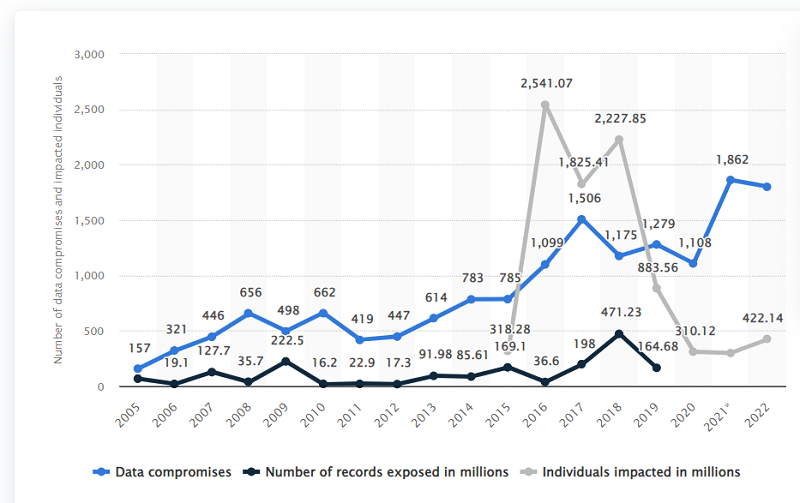
In this era of digital age, businesses must take care of their customer data promptly and proactively before it is breached. With cybercrime growing in America more than ever, especially in the healthcare, financial services, and manufacturing industries, all types of businesses have found a need for security solutions that can help them keep their client’s sensitive information at least secured.
It is worth mentioning that in 2020, the most extensive breach exposed over 11 billion records by an Adult streaming site CAM4. This case stands out, as cybersecurity researchers discovered the vulnerability ahead of cyber criminals. Yahoo’s famous hack in 2013 was the second-largest of all time, where one billion were reported as breached, only for this figure to triple after further investigation.
Average Cost of a Data Breach
The average cost of a data breach in 2020 was $3.86 million
The Ponemon Institute’s 2020 Cost of a Data Breach Report reveals an average cost of 3.86 million USD for data breaches in the US, highlighting the significant impact these events can have on businesses and demonstrating why robust security automation and incident response strategies are essential to mitigating such risks.

Results showed that organizations without these safeguards experienced higher remediation costs, reaching 8.64 million dollars – up by 5% compared with 2019 figures.
Sponsored by IBM for the last five years, The Ponemon Institute’s report highlights that organizations without security automation and incident response mechanisms have a notably higher remediation cost.
With the global average price tag going up, Canada ($6.03 million), Japan ($5.24 million), and the Middle East ($6.52 million) experienced notable increases in their localized costs, too – while healthcare came out on top at $7.1M followed closely behind by energy industry firms costing an average of $6.39million per breach respectively according to the latest research published this year from IBM Ltd.
Average Time to Identify Data Breaches
It took 280 days to identify and contain a breach in 2020
However, current organizations are at great risk for data breaches, leading to expensive incidents to resolve and remediate.
According to the study in 2020, the average global cost incurred translated into $3.86 million for an incident, with this amount ballooning up to $8.64 in the US; longer detection times tack on spend as well, with processing times documented at 280 days.
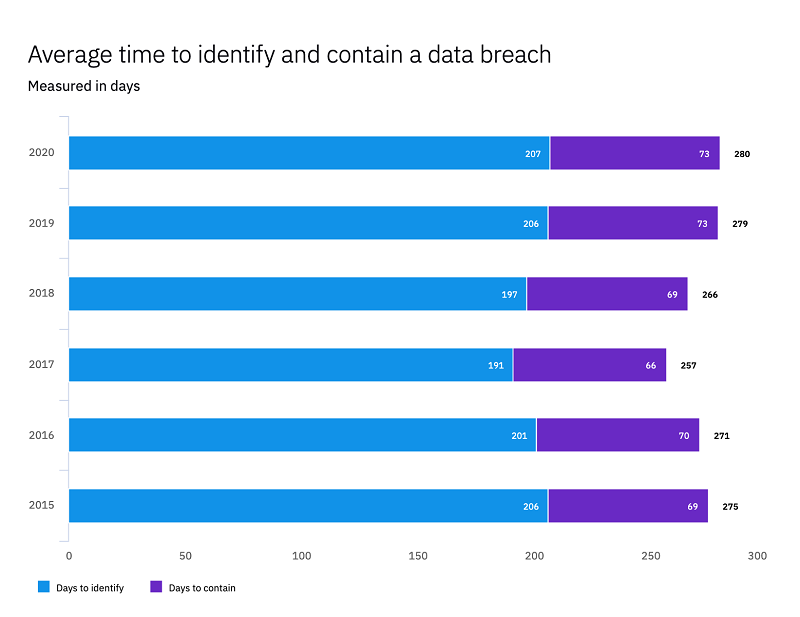
To effectively minimize risks and reduce damage caused by cyber threats, it is important that any organization invest heavily in robust cybersecurity infrastructure supported further by measures such as tests for incident response preparedness and red team testing alongside sharing threat intelligence and instituting data loss prevention solutions/strategies.
Indeed, Research found that adding an incident response plan could reduce breach costs by up to $2 million compared to no protection – leading to potential savings of between $3.29-$5.29 million per attack occurrence.
Ransomware Attacks Worldwide
Annual number of ransomware attacks worldwide from 2017 to 2022
Ransomware attacks that incriminate huge volumes of data are a challenge for global organizations every day, and they can be fatal to business operations.
As provided by Statista in worldwide figures, there have been recorded 493.33 million attempts globally till 2022, where manufacturing has become the most damaged sector (437 incidents).
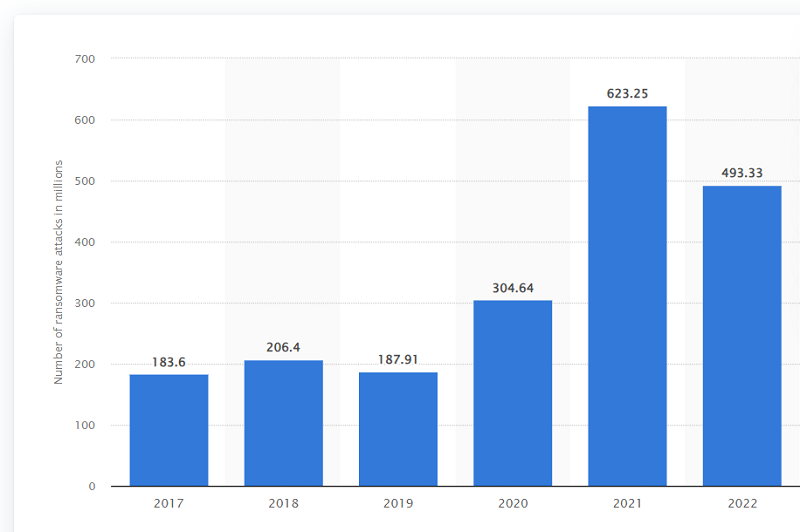
There are growing incidents of ramson ware attacks across all sectors and all types of organizations, irrespective of size and industry. As per Statista, in 2017, the ransomware attacks were 183.6 million, and it reached 623.25 million in 2021.
North America was overly impacted due to its higher percentage of critical infrastructure organizations that saw a considerable share in the ransomware attacks reported; US public health and healthcare entities registered the highest complaints about these types of cybercrime assaults over other sectors.
In safeguarding against such damages proactively or reducing them, businesses must be active in avoiding further exposure to future risks.
Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) is an alarming business model whose existence has been in operation for some time now. It entails hackers who develop attack models that they sell off to affiliates targeting unsuspecting victims.
Phishing Attacks on the Rise
74% of organizations in the U.S. were victims of phishing attacks in 2020
Phishing is a growing threat across the globe, with employees receiving an average of 14 malicious emails per year, according to Tessian research. 96% of all phishing attempts are done through email, while 3% and 1% occur via malicious websites or telephone, respectively.
ESET further reported a 7.3 % increase in said attacks between May and August 2021 alone, the majority targeting businesses rather than consumers.
Specific regional data indicates that 74%, 66%, 60%, 56%, 51%, 48%, and 47% of companies based in the US, UK, Australia, Japan, Spain, France and Germany experienced successful cyber-attacks throughout 2020, respectively, showing just how pervasive this issue has grown over time. It is no wonder that anti-phishing tools are now considered an integral part of security measures for businesses.
Tessian’s 2021 research reveals that workers in industries such as retail, manufacturing, and food and beverage received a significant quantity of malicious emails each year.
An average of 49 malicious emails per worker were found for the retail industry specifically, with tech (14) receiving fewer on average. Furthermore, PDFs were the most common type of file attached to phishing emails – trusted yet versatile files capable of concealing fraudulent links and scripts alike.
IoT Threat
By 2030, there will be 29.42 billion Internet of Things (IoT) connected devices
The use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has been steadily increasing in recent years, and with Statista projections expecting the number to nearly double from 15.1 billion connected devices in 2020 to over 29 billion in 2030, there are plenty of opportunities for businesses across virtually every industry vertical and consumer markets.
In 2020, consumers accounted for 60 percent of all IoT device connections; this share will remain stable throughout the next decade at least.
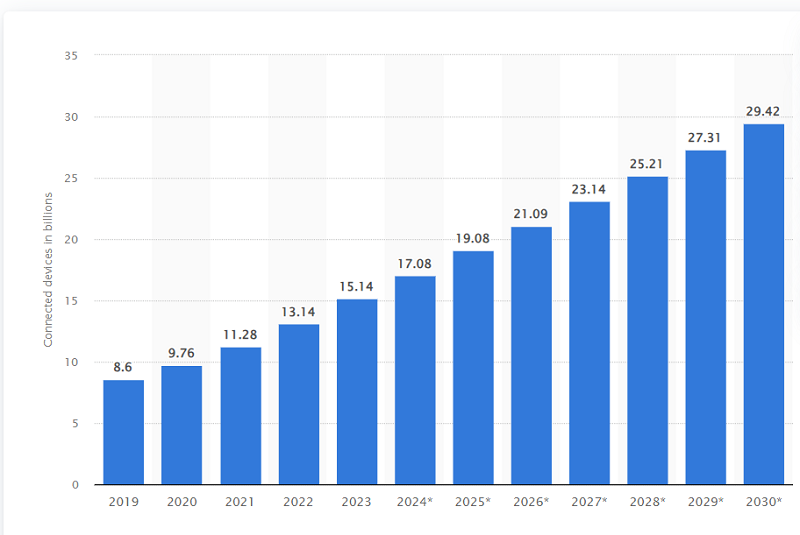
Currently, electricity, gas, steam, A/C systems, etc., have more than 100 million such devices running on them already. Overall, IoT devices across all industry verticals are predicted to grow to more than 8 billion by 2030.
Smartphones comprise an important majority of the use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which are estimated to reach up to five billion connected units globally.
By 2025, 90% of the organizations that fail to control public cloud use will inappropriately share sensitive data
With ongoing public cloud use continuing to increase, Gartner predicts that 90% of organizations that fail to control it will be at risk for a data breach. This unnecessary risk exposure is the result of lagging strategies and inadequate governance models, which can lead to misconfigurations or third-party mistakes, resulting in serious security issues if not addressed quickly enough.
To prevent this from happening, CIOs need an enterprise strategy before proceeding with any form of public cloud implementation.
As such, Garter provides sound guidance moving forward so organizations are equipped with both knowledge and advice on developing secure cloud computing solutions as well as predictions about what trends await us within the industry for future consideration when managing security risks associated with untamed usage of public clouds.
However, due to the inherent ambiguity and security issues that come with it, many CIOs are hesitant when considering leveraging public cloud services. This is why every enterprise should have agreed upon plans and policies on security; such steps will ensure appropriate risk mitigation levels based on their budget and appetite capacity.
Ultimately, no form of security protection provides perfect coverage, so well-calculated decisions must still be made, allowing enterprises as much control over risks while gaining maximum value from using Cloud Computing strategically within their organization.
Data Breaches Due to Inefficient Passwords
81% of data breaches are due to weak, reused, or stolen passwords
Password management can be challenging for businesses, both domestically and abroad. The Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report found that an alarming 81% of hacking-related breaches were by dictionary attacks caused by either stolen or weak passwords.
To make matters worse, 70% of employees reuse their work passwords across multiple accounts, and 91% know it’s bad practice – yet still, 59% don’t take the necessary precautions to protect themselves online.
Organizations must understand that employee negligence is a major factor when it comes to data security breaches, and consequently should prioritize implementing strong policies along with educating staff on how to manage their passwords effectively to safeguard against digital risks from within the business structure itself as well as externally.
There was a 600% increase in cyber threats during the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic and more remote activities, such as teleworking, have opened up a new avenue for cybercriminals to take advantage of. Enisa’s report indicates that since February 2020, there has been an alarming 600% spike in email phishing attacks globally.
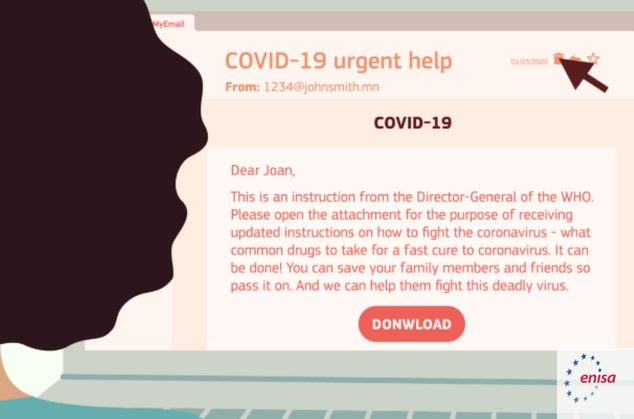
Almost 2% out of 468000 global emails were classified under COVID-19, ranging from 54% categorized as scams, 34% as brand impersonation attacks, 11% blackmail, and 1% as business email compromise (BEC).
Cybercriminals use people’s naivety by making them reveal their personal information, click on malicious links/attachments, and download malware into computers without their knowledge. Therefore, organizations and companies must secure against these kinds of attacks.
Fraudulent actors disguise themselves as government organizations and essential figures to provide perceived legitimacy. Carefully crafted emails feature logos and branding of the purported organization, making them appear genuine.
Rise in DDoS Attacks
DDoS attack numbers grew by 151% in the first half of 2020 compared to the same period in 2019
Neustar, Inc., an innovative information services and technology leader in identity resolution, has just released its cyber threats report, which points to significant shifts in distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack patterns from the first half of 2020.
According to Neustar’s Security Operations Center (SOC), DDoS attacks have surged 151% compared with 2019, including a record 1.17 Terabits-per second and 5 days and 18 hours long duration – representing the growing number and intensity of network-related cyberattacks as more people rely on the internet during remote working operations.
Leveraging Ultra DNS Network and UltraDDoS Protect service for navigating through Internet requests along with detecting threats makes Neustar aptly positioned to observe macro trends emerging at the networks’ level due to COVID disruptions globally.
Increase in Healthcare Breaches Due to Human Error
Basic human error accounted for 31 percent of Healthcare breaches
Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report (2020 DBIR) report shows that financial gain is the primary driver for cybercrime. The report analyzed over 32,000 security incidents and found that 86% of breaches were financially motivated.

The 2020 DBIR is a detailed analysis of 16 industries. It reveals the variations in security challenges and incidents across sectors, with ransomware being involved in a higher percentage of malware incidents in the Public Sector and educational services than in Manufacturing, while errors caused more breaches from within the latter industry compared to external sources.
The report also reveals that the majority of these were committed by external actors – 70 percent – and largely organized crime at 55%. Furthermore, credential theft and social engineering attacks such as phishing or business email compromises made up over 67% of them, 37% from stolen credentials and 25% due to phishing scams.
Basic human errors account for 31% of all data breaches, while 51% are caused by external attacks. Insiders also pose a risk with 48%, making access to credentials even more important in maintaining safety standards.
With external and internal breaches on the rise, healthcare remains one of the most vulnerable sectors when it comes to cybersecurity.
What Cybercrime Costs the World
Cybercrime To Cost The World $10.5 Trillion Annually By 2025
Cybercrime is a growing economic threat, costing the world trillions of dollars each year and shows no signs of stopping.
Cybersecurity Ventures predicts that by 2025, cybercrime will reach an annual cost as high as $10.5 trillion USD globally, which is 15 percent higher than 2015’s estimated $3 trillion USD losses caused by criminals hacking businesses, both large and small worldwide.
We are entering an era of unprecedented data expansion, with the cloud predicted to house 100 zettabytes by 2025 – 50 percent of the world’s total stored data.
This includes public clouds operated by tech giants, government-owned clouds accessible to citizens and businesses, corporate private clouds, plus those from dedicated storage providers.
In addition, cyber threats have diversified beyond computers and networks into targeting Things such as cars, power grids, etc., which often connect back in some way to business systems, making cybersecurity ever more complex.
This extraordinary transfer of wealth poses serious risks to investment incentives, making it one of the most damaging forces in history comparable to natural catastrophes; yearly costs combined together multiplied exponentially due to an even wider attack surface available for exploitation in just five years from now.
Shortage of Cybersecurity Jobs
There is a projected shortage of 3.5 million cybersecurity jobs by 2025
The cybersecurity job market has grown exponentially in recent years; Cybersecurity Ventures reported a 350 percent increase – from one million openings in 2013 to 3.5 million vacancies by 2021.
Recent years have seen the number of unfilled jobs stabilize at this level, with more than 750,000 available positions in the U.S. alone – an outlook that looks set to remain unchanged through 2025 due largely to industry efforts failing to outpace rising demand.

With tech professionals expected not just to excel in their respective fields but to become equally proficient defenders of security threats such as phishing scams, BEC frauds, and social engineering attacks – it’s increasingly evident every IT specialist now doubles up as a cyber professional, regardless of background or sector focus.
In this extremely competitive field where unemployment rates are near zero, those looking to enter must possess extensive backgrounds while accepting additional responsibility for protecting today’s infrastructure against malicious actors seeking access.
Industrial Computers Hacked by Malicious Software
34% of industrial computers were attacked by malicious software in the second quarter of 2023
Kaspersky’s security solutions blocked a record-high 11,727 different malware families in industrial systems during the first half of 2023. This marks two consecutive halves with increased levels of malicious activity on Industrial Control Systems (ICS), according to Kaspersky’s ICS CERT Landscape Report.
In Q2 alone, 26.8 percent of computers had been affected by various forms of malicious objects – the highest recorded number since 2019.
The report also shared further details like attack methods and motives behind these threats against industrial computing to provide better protection for creating secure business environments worldwide.
Cyber threats remain an ever-present worry in the Building Automation sector, with 38.5 percent of computers attacked this year alone. However, other industries like Energy and Oil and gas have seen opposite trends since 2021 – a 36 percent increase for Energy and a 30.8 decrease for oil and gas.
Engineering, ICS integration, manufacturing, and Energy sectors also saw an overall rise in the percentage of blocked malicious objects during H1 2023 across all networks worldwide.
With alarming figures like these, it’s no surprise that businesses are increasingly prioritizing cybersecurity measures and risk assessment to protect their most sensitive data from potential harm or loss due to external attacks or criminal activities online.
Education Highly Vulnerable to Malware
Education is globally the sector most vulnerable to threats like malware: 84% increase in attacks over a 6-month period
New research by Malwarebytes came up with stats that shocked educational institutions hit with ransomware attacks from June 2022 through May 2023.
In fact, the known number of those assaults surged by 84%, with one gang, Vice Society, responsible for 23% alone. This was among the third-highest increase among all sectors monitored.

Of this activity, the USA, and UK accounted for 56% and 15%, respectively. At the top spot taking these targeted strikes were five other gangs: LockBit (33), BianLian (18), Royal (16), and AvosLocker (15). These findings show a worrying trend targeting more education as its preferred sector-wide victim in the world today.
In terms of the time and cost spent, a ransomware attack can be devastating — schools within the United States experienced an estimated 1,600 days of downtime with a $4.54 million average expense due to such attacks in 2022.
27% of breaches in 2019 involved social engineering techniques
Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report provides insight into the tactics and pathways used by cyber-criminals to target companies of all sizes with hacking, phishing, and attacks on cloud-based data.
The report combines 32,002 security incidents across 81 countries worldwide, along with 3,950 confirmed breaches.

Findings show that 86 percent of these were for financial gain – up from 71 percent in 2019 – making clear the need for a strong focus on remote working security.
The 2020 DBIR provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of security, analyzing 16 individual sectors across various industry verticals. This data shows considerable variation in threat levels between industries; for instance, ransomware attacks on Manufacturing accounted for only 23%, while they were as high as 80% within Educational Services and 61% among public sector organizations.
Additionally, errors caused 33% of breaches in Public Sector environments compared to just 12% in Manufacturing ones. Furthermore, social engineering accounted for 27 percent of incidents; throughout all these findings lies an important reminder: Security is not something that can be taken lightly by any organization today.
AI Cybersecurity Market
Global AI in cybersecurity market is expected to reach $60.6 billion by 2028
With the relentless rise of cybercrime across the world, AI in cybersecurity provides advanced technology to businesses as well as individuals.
As per marketsandmarkets, with a valuation of USD 60.6 billion that is forecasted to reach by 2028, the industry has marked quick growth due to the growing adoption of connected IoT devices, higher prevalence of cyber threats and data privacy concerns, and Wi-Fi vulnerabilities demanding sophisticated security measures.
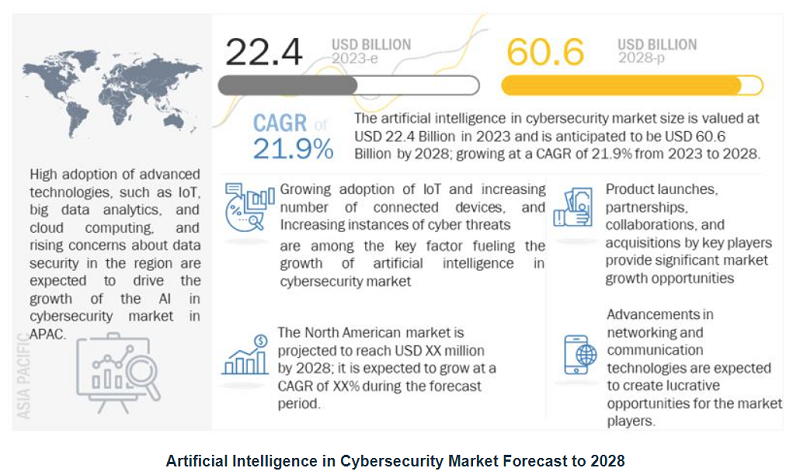
It offers automated assessment methods with vast improvements in accuracy levels while decreasing false alarms through artificial intelligence deployment yet providing adequate protection against complex attacks coupled with better operational efficiency and efficacy together.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a key ingredient in dealing with changing cyber threats as the need for more sophisticated security solutions and advancements in AI technology gather pace.
Riding on increased investment and innovation, the AI-driven cybersecurity market is poised for further growth even while it automates manual tasks that need to be attended to by human beings and becomes better at detecting and responding to threats.
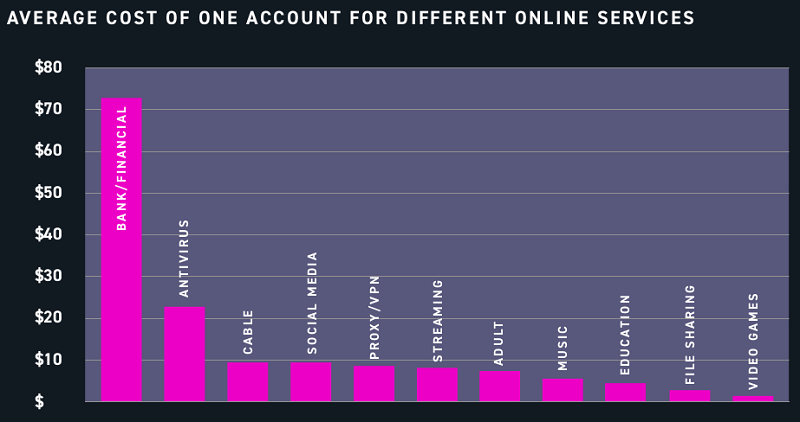
Worth of Stolen Credentials on Dark Web
15 billion stolen account credentials were available for purchase on the dark web in 2020
As per Wired News, Cybercriminals have an abundance of stolen login credentials available to them, with approximately 15 billion circulating on hacker forums. These are from over 100,000 data breaches and include 5 billion unique passwords.

Login pairs for non-financial services such as cable, streaming platforms, or adult sites tend to be the cheapest; however, advertisements offering corporate accounts that can access financial systems are also common at a higher average price of $70.91 per account.
Domain administrator access is highly valued due to their trustworthiness and control levels – often reaching up to $120,000 – while victims include large organizations from across sectors such as petrochemical, cybersecurity, petroleum companies, or universities. Governments have also been targeted through these criminal auctions.
Digital Shadows report confirms an overwhelming presence of this malicious activity in today’s cybercriminal marketplaces, making it even more essential for organizations to establish strong cybersecurity measures against these threats.
Also read: How Much is Your Personal Information Worth on the Dark Web?
Final words
Cybersecurity practices are needed to protect digital assets that range from sensitive personal and financial information to intellectual property and critical infrastructure. Without proper measures concerning cyber-attacks, there can be severe consequences, such as financial loss or even physical harm – due to reputational damage.
Written above are various research reports showing that data and user privacy are always at risk, so security solutions must be applied for better protection of all information and data.
Next up, check out these cyberattack simulation tools to improve security.


