DDoS attacks threaten the security landscape of websites and cause damage in terms of data leaks, reputation, and finances; to name a few.
Even a small vulnerability in your application or network can lead to serious problems like DDoS attacks. The primary target of this type of online attack is to slow down or take down a website by flooding the entire network with fake traffic.
Therefore, website owners must be aware of different types of DDoS attacks and have the capability of mitigating them or at least minimizing their impact.
Learn the difference between DoS and DDoS attack.
In this article, I’ll discuss different types of DDoS attacks and how to prevent them and safeguard your website.
But first, let’s understand the basics.
What Is a DDoS Attack?

A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is a security threat to websites that can disrupt the traffic of the server, network, or service by overwhelming the surrounding infrastructure or target with an unwanted flood of traffic. It can exploit computers and other related network resources, like IoT devices.
The main goal of a DDoS attack is to flood the system with fake traffic, such as a sudden increase in connection requests, messages, or packets. This massive amount of requests can cause the systems to crash or slow down as the resources won’t be enough to accommodate the requests.
Although some hackers use this attack to blackmail website owners into paying hefty sums, the main motives behind the attack are:
- To disrupt communications and services
- To inflict damage to your brand
- To gain an advantage from your business
- To distract the incident response team
Businesses of all sizes can get affected by these attacks if they do not follow the proper security measures. The most targeted businesses are:
- Online retailers
- Fintech and financial companies
- Online gambling and gaming companies
- Government entities
- IT service providers
Generally, attackers use a Botnet to carry out such attacks. Botnet is linked to malware-infected computers, IoT gadgets, and mobile devices which are under the DDoS attacker’s control. Hackers use these network devices to send multiple requests to a server IP address or a target website.
Learn how to secure router against Mirai Botnet attacks.
Due to DDoS attacks, company owners face numerous difficulties, such as abandoned carts, loss of business and revenue, discontinuation of services, frustrated users, and more. This will require you to spend significant money and time to get your business back to its previous stage and achieve growth.
How Does a DDoS Attack Happen?

Attackers use internet-connected “zombie” machines to carry out DDoS attacks. The networks of these machines consist of numerous devices, like IoT devices which can be infected with malware, letting attackers control your systems remotely.
These individual devices are known as bots, and a set of bots is known as a botnet. Once the attacker can establish a botnet, it will be easier for them to direct an attack through remote instructions.
When a victim’s network or server is targeted, every bot in the botnet sends a request to the website’s IP address, causing the network or server to become jammed with traffic. Since each bot is a single internet device, it is difficult to separate normal traffic from attack traffic.
Impact of a DDoS Attack on a Business

DDoS attacks slow down your website’s performance, cut off customer services, and cause more problems. Due to this, businesses face a lot of trouble, such as:
- Loss of reputation: Reputation is a major aspect of every business. Customers, investors, and partners trust your website and rely on them. But when your site faces DDoS attacks, it sends them an idea that your site is not secure. Thus, it becomes difficult to handle your reputation.
- Data loss: Hackers can gain access to your systems and data and misuse it to steal money from bank accounts and perform other mischievous activities.
- Financial loss: Suppose you have an e-commerce platform or website that suddenly goes offline; you start losing money as requests and orders can’t be processed further. In such scenarios, competitor websites gain the trust of your customers. In addition, getting back your lost business, customers, and reputation also cost you more.
Main Types of DDoS Attacks
Although the primary goal of every DDoS attack is to overwhelm your entire system with fake traffic, how it’s done differs. Let’s discuss the three broad types of DDoS attacks:
#1. Application Layer Attacks
The application layer is the layer where the server generates a response to the incoming request from a client server.
For example, if you enter https://www.abc.com/learning/ on your web browser, it will send an HTTP request to the server and requests the learning page. The server will search all the information related to this page, packages it, and sends it back to your web browser.
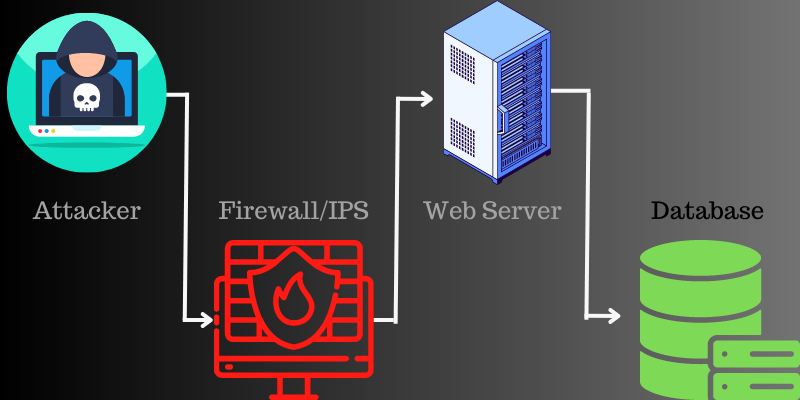
This fetching and packaging process happens on this layer. The attack on the application layer occurs when an attacker uses multiple machines/bots to repeatedly send requests to the same source of the server.
Thus, the most popular application layer attack is the HTTP flood attack, where malicious actors keep sending unwanted HTTP requests to the server using a wide range of IP addresses.
#2. Volumetric Attacks
In volumetric attacks, attackers bombard a server with numerous traffic so that the bandwidth of the website gets exhausted completely.
The most common attack that attackers use is the DNS amplification attack. Here, a malicious actor continuously sends requests to the DNS server using the fake IP address of the targeted website.
The DNS server sends the response to the server targeted by the attackers. When done multiple times, the target server is confused and slows down, resulting in poor performance of the website.
#3. Protocol Attacks

Protocol attacks exhaust the networking systems like routing engines, load balancers, and firewalls along with the resources of the server. When two computers initiate a communication channel, they do a TCP handshake. This means two parties exchange their preliminary information.
The SYN packet is the first step towards the TCP handshake, where the server knows that the client needs to start a new channel. In a protocol attack, the hacker floods the server or networks with multiple SYN packets containing fake IP addresses.
The server will respond to every packet, requesting to complete the handshake. However, in this case, the client will never respond to the packets, letting the server wait for too long to get the response. This can slow down the performance of the server.
Different Types of DDoS Attacks
The three attacks I discussed above are further divided into different types of attacks, such as HTTP flood, DNS flood, SYN flood, Smurf, and more. Let’s discuss them and how they can impact your business.
You should check out how to protect from Smurf attacks.
#1. HTTP Flood
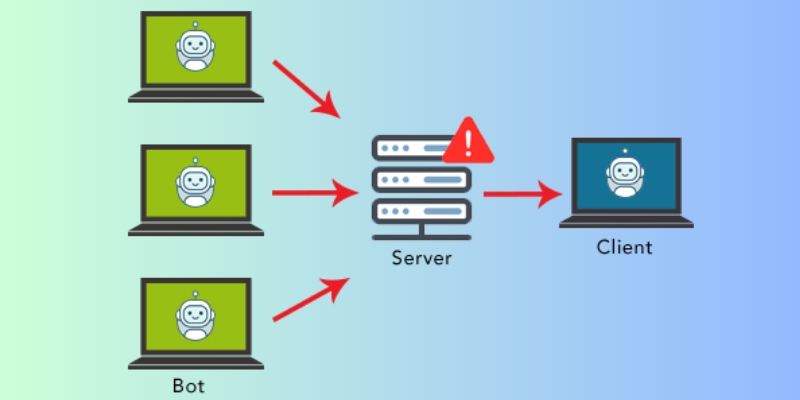
HTTP is the common base of browser-based requests, which is commonly used to open webpages or send content over the internet.
An HTTP flood is a type of DDoS attack coming under volumetric attacks. These are specially designed to overload the targeted server with too many HTTP requests. Once the targeted server has been loaded with requests and can not respond, DDoS will send additional requests from real users.
#2. DNS Flood
Domain Name Systems (DNS) are like the phonebooks of the internet. Also, they behave like a path where internet devices look up some specific web servers to access internet content.
A DNS flood attack is a type of DDoS attack where the attacker floods a specific domain’s DNS servers, targeting it to disrupt DNS resolution.
If a user doesn’t have a phonebook, finding the address to make a phone call will be difficult for a particular resource. A similar thing happens in the DNS Flood scenario. Hence, a website will be compromised, and it won’t be able to respond to legitimate traffic.
#3. Ping Flood
The ICMP is an internet protocol layer used by different network devices in order to communicate between them. Often, ICMP echo-reply messages and echo requests are commonly used to ping a device to know the connectivity and health of the device.
In the Ping Flood attack, the hacker attempts to overload a targeted device with echo-request packets. This makes the target incapable of accessing normal heavy traffic. When fake traffic comes from numerous devices, the attack forms a DDoS attack.
#4. SYN Flood
An SYN flood is a type of DDoS attack, also known as a half-open attack, that aims to make the server unavailable to divert legitimate traffic and consumes all the server resources available.
By continuously sending initial connection request packets, the hacker can overload all the ports on the server machine. This enables the device to respond to legal traffic sluggishly or yield no response at all.
#5. UDP Flood
In a UDP flood attack, a wide range of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets are sent to the server with the goal of overloading, which reduces the device’s ability to respond and process.
The firewall becomes exhausted, resulting in a DDoS attack. In this attack, the attacker exploits the server steps taken to respond to UDP packets that are already sent to the ports.
#6. DNS Amplification Attack
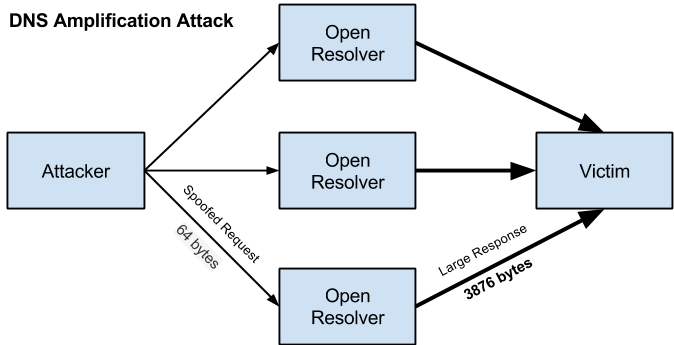
A DNS amplification attack is a volumetric DDoS attack where the attacker uses the functionality of open DNS to overload the target network or server with the amplified traffic amount. This makes the server, along with its surrounding infrastructure, inaccessible.
Every amplification attacks exploit a discrepancy in the consumption of bandwidth between the targeted web source and an attacker. As a result, the network becomes clogged with fake traffic, causing DDoS attacks.
#7. XML-RPC Pingback
A pingback is a type of comment which is created while linking to a specific blog post. XML-RPC pingback is a common functionality of the WordPress module. This functionality can be used easily by attackers to use the pingback feature of the blog site in order to attack third-party sites.
This can lead to many different attacks as it exposes your site to attract various attacks. Some attacks are Brute Force attacks, Cross-site port attacks, Patsy proxy attacks, and more.
Explore Brute-force attack tools for pen test.
#8. Slowloris DDoS Attack
Slowloris is a type of DDoS attack that allows a hacker to overload the targeted server through many openings and maintain different HTTP connections simultaneously between the target and the attacker. It comes under an application layer attack that occurs by using partial HTTP requests.
Interestingly, instead of a category of attack, Slowloris is an attack tool specifically designed to enable a single machine to bring down the server. This type of attack requires low bandwidth and aims to use server resources.
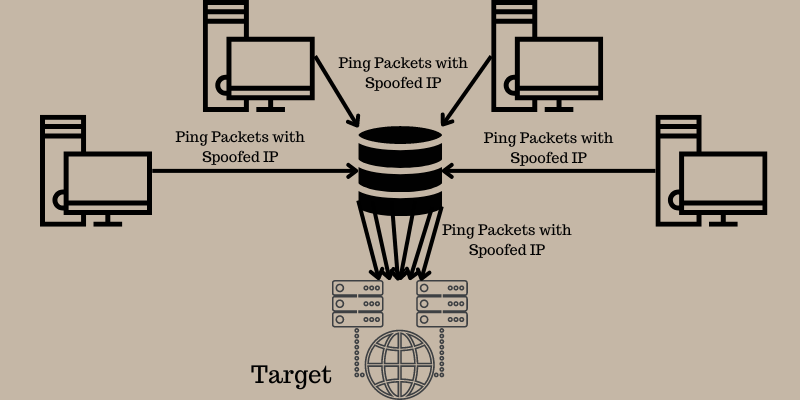
#9. Smurf DDoS Attack
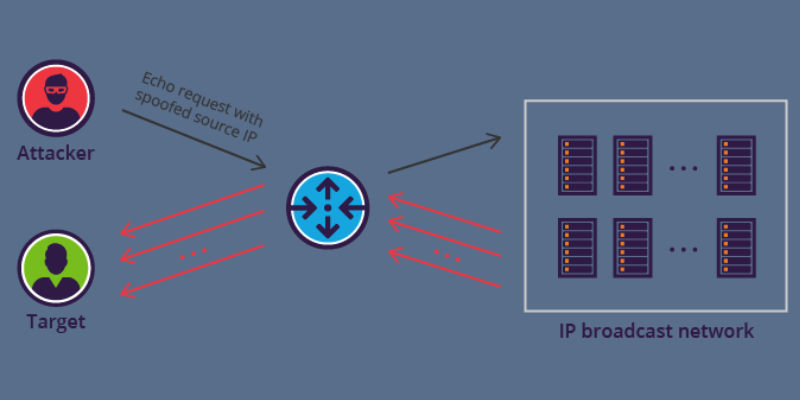
A Smurf attack occurs at the network level. This name came forward after malware, DDoS.Smurf, that enables attackers to execute the attack. The attackers aim to target bigger companies in order to take them down.
A Smurf attack is similar to a ping flood attack that uses ICMP packets to overwhelm computers and other devices with ICMP echo requests. This is how the attacks occur:
- First, Smurf builds a fake packet having a source address set as the real IP address of the victim.
- The packet is sent to the IP broadcast address of a firewall. In return, it sends back the requests to each host device inside the network.
- Each device receives numerous requests, resulting in compromising legitimate traffic.
#10. Zero Day Attack
A zero-day defines security flaws in firmware, hardware, or software, which are unknown to the parties responsible for fixing the flaw. A zero-day attack refers to the attack that is carried out between the time vulnerability is uncovered and the first attack.
Hackers take advantage of the vulnerability and execute the attack easily. Once this vulnerability becomes public, it is called a one-day or n-day vulnerability.
Now that we know about different types of attacks, let’s discuss some solutions to mitigate them.
Solutions for Application Layer Attacks
For application layer attacks, you can use a web application firewall. The below solutions offer web application firewalls (WAF) that you can use to prevent attacks.
#1. Sucuri
Protect your websites from attacks with Sucuri’s Website Application Firewall (WAF), which eliminates bad actors, enhances your website availability, and speeds up the load times. To activate the firewall for your website, follow these steps:
- Add your website to the Sucuri WAF
- Protect incoming data by creating SSL certificates for the firewall server
- Activate the firewall by changing the DNS records
- Opt for high-performance caching to maximize site optimization
Choose Sucuri’s Basic or Pro plan and secure your website from unwanted attacks.
#2. Cloudflare
Get enterprise-grade security with Cloudflare WAF solution and experience better security, powerful protection, fast deployment, and easy management. It offers zero-day vulnerability protections.
According to leading analysts, Cloudflare is an application security expert. You will get machine learning capabilities developed and trained by experts to protect your site from threats, catch evasions, and more.
Solutions for Volumetric and Protocols Attacks
For volumetric and protocol attacks, you can use the below solutions to protect your website from DDoS attacks.
#1. Cloudflare

Get industry-leading DDoS prevention from Cloudflare to safeguard your website and prevent losing customers and their trust. Its 197 Tbps network blocks more than 112 billion daily threats. The global network of Cloudflare spans 285+ cities and 100+ countries to prevent attacks.
Onboarding is simple and easy; use Cloudflare’s dashboard or API and add Cloudflare performance, reliability, and security functionality to your website. Doing this can mitigate website, application, and network DDoS attacks.
#2. Sucuri
Enhance your website’s performance and availability against large attacks with Sucuri’s Anycast Network and secure content delivery solution. It maintains your website’s health even during massive DDoS attacks and high traffic spikes.
#3. Imperva
Secure all your assets from DDoS attacks with Imperva and ensure your business continuity with an uptime guarantee. It minimizes downtime and bandwidth costs, gives unlimited protection against DDoS attacks, and ensures website availability without impacting performance.
Conclusion
DDoS attack is a deadly cybercrime where the hacker floods a server with fake massive traffic so that real users face difficulty in accessing sites and online services. There are many kinds of DDoS attacks targeting HTTP, Ping, SYN, and more to slow down your website performance.
Discussed above are some of the best solutions to fight against application, volumetric, and protocol attacks. They help prevent unwanted traffic coming from different sources to retain the bandwidth and eliminate downtimes.

