Ransomware attacks are a type of cyber threat, increasing worldwide and targeting individuals, businesses, and even government institutions.
Your data and systems can be held hostage in the blink of an eye, leaving you powerless and frustrated.
Imagine you wake up and find that all your valuable files, including family photos, important documents, and cherished memories, have been encrypted. You receive a digital ransom note demanding payment for their release.
This is not just terrifying but a harsh reality that thousands of people have faced. As a result of these ransomware attacks, people not only have lost huge amounts of money but also data, reputation, and whatnot.
This is why it’s essential to strengthen your digital defense mechanisms, and responding to these relentless criminals is of utmost importance.
For this, everyone should understand how these cyber attacks work so they can better protect themselves against the attacks.
In this article, I’ll discuss the most common types of ransomware along with essential strategies and practices to shield yourself from falling victim to these cyber traps.
Let’s get started!
What Is a Ransomware Attack?

A ransomware attack is a type of cyberattack involving a digital scenario where the attacker gains access to your systems or resources and encrypts your important files, locking you out and holding your data hostage.
Then comes the demand: pay up or bid your data goodbye.
It’s a sudden and shocking moment that can occur via harmful links, email attachments or compromised websites. These attacks don’t discriminate – they hit individuals and businesses, causing chaos and data loss. So, prevention is key.
The types of ransomware are:
- Encrypting ransomware
- Scareware ransomware
- Locker ransomware
- Master Boot Record ransomware
- Mobile Ransomware
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
- Petya Ransomware
We talk about them in detail later in the article.
Growing Threat of Ransomware Attacks

Understanding the escalating dangers of ransomware attacks is vital, given their rising prevalence and potential for severe repercussions. Cybercriminals are continuously enhancing their tactics and targets, extending beyond individuals to businesses and organizations.
According to Statista, around 70% of organizations worldwide suffered some kind of ransomware attack.
Ransomware attacks can have devastating consequences, causing loss of data, financial setbacks, and disruptions to daily operations. These attacks typically exploit system vulnerabilities and are often spread through email attachments or malicious websites.
Importance of Understanding Ransomware Attacks
Understanding ransomware attacks is crucial for your digital safety. Here are four reasons why:
Prevention
Knowledge about how ransomware works empowers you to take preventive steps. You can identify suspicious emails, links, or attachments and avoid falling victim.
Protection

Being informed about what’s going on in the world of cyberattacks helps you take effective strategies that can protect your personal and sensitive data. You’ll know to back up your files regularly, making it easier to restore them even if an attack occurs.
Business Impact
For businesses, ransomware can cause operational disruptions and result in financial losses. Having an understanding of these attacks enables you to establish and implement strong cybersecurity strategies, ensuring the protection of your company’s data and reputation.
Response
In case you’re targeted, knowing about ransomware gives you the upper hand. You can respond promptly, report the incident to authorities, and decide whether to pay the ransom or not.
How Do Ransomware Attacks Work?
Ransomware attacks usually start with malicious software, frequently concealed as seemingly harmless emails or downloads. Once triggered, the ransomware locks your files, rendering them unreachable.
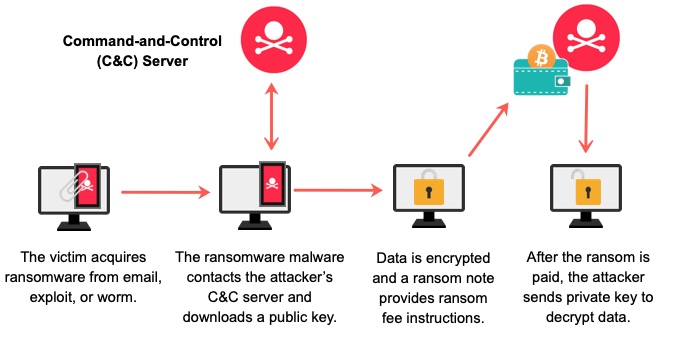
Subsequently, you are presented with a demand for ransom, typically in cryptocurrency, in return for a decryption key to get your data back.
Ransomware exploits vulnerabilities in your system’s software or your own actions, like clicking on suspicious links. It has the ability to rapidly propagate across networks, impacting not only individuals but also businesses and institutions.
Ransomware attacks come in various forms, each with its own tricks and tactics to hold your data hostage.
Here are the most common types of ransomware attacks and their examples, prevention, and responding to them.
Encrypting Ransomware

This is a form of harmful software that uses encryption to lock your files.
These attacks commence when you unknowingly download infected attachments or visit compromised websites. The encryption process renders your files unreadable until a ransom is given.
It’s a hostage situation for your digital stuff. It is like a digital lock that cyber criminals put on your files. It enters into your device and encrypts your important documents, photos, and data. You can’t open or use them anymore. They require payment from you in exchange for providing the key to unlock your files.
Examples of Encrypting Ransomware
- WannaCry: It affected thousands of computers in 2017, exploiting a Windows vulnerability.
- CryptoLocker: One of the first major ransomware attacks, CryptoLocker, emerged in 2013 and targeted Windows users.
Prevention
- Keep your operating system and software up to date to fix any vulnerabilities.
- Be cautious, and avoid opening email attachments or clicking links from unknown sources.
- Frequently create backups of your crucial files on an external storage device that is not linked to your network.
Response
- Isolate the infected system by unplugging it from the network to prevent the ransomware from spreading.
- Don’t pay because there’s no guarantee you’ll get your files back, and paying encourages more attacks.
- Inform law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity experts about the attack.
Scareware Ransomware
It is deceptive software that tricks you into believing your computer is infected with viruses or other threats. It aims to scare you into paying money to remove the supposed threats.
This ransomware messes with your mind. It throws fake alarms and scary messages on your screen, making you think your device is under attack. But here’s the trick: it’s all fake.
The attacker wants you to pay to remove these made-up threats. Stay cool, don’t fall for the scare. Keep your software updated and trust reliable security tools to keep you safe.
Examples of Scareware Ransomware
- FakeAV: FakeAV displays fake antivirus warnings and prompts you to pay for a solution.
- WinFixer: Shows false system errors and offers to fix them for a fee.
Prevention
- Stay informed of common scare tactics, and don’t trust sudden alarming pop-ups.
- Use only legitimate software downloaded from official sources to avoid malicious downloads.
- Install reliable and powerful antivirus software in your systems to detect and block scareware.
Response
- Ignore scareware messages, and don’t pay any money.
- Close the browser or application if a scareware pop-up appears.
- Scan Your System: Conduct comprehensive system scans frequently using your antivirus software to ensure the security of your computer.
Locker Ransomware

It’s a form of malicious software that effectively blocks access to your entire computer or device, making it unavailable until a ransom is paid.
This ransomware means you are being “locked out” of your device. It takes over your device, making everything inaccessible – your files, apps, everything. They ask you to make a payment to regain access.
Examples of Locker Ransomware
- Police-themed Ransomware: Pretends to be law enforcement, accusing you of illegal activity and demanding payment.
- Winlocker: Locks your computer’s operating system, preventing you from accessing anything.
Prevention
- Create complex and strong passwords to increase the difficulty of unauthorized access attempts by attackers.
- Make sure to regularly update your operating system and software to address any vulnerabilities.
- Frequently create backups of your crucial files on an external storage device that isn’t linked to your network.
- Rely on trusted security tools to prevent these digital padlocks from taking control.
Response
- Do not make the payment, as there is no assurance that you will regain access.
- Initiate a safe mode restart of your computer to remove the ransomware.
- Use antivirus software to scan and remove the ransomware.
Master Boot Record Ransomware

Master Boot Record (MBR) ransomware targets the Master Boot Record of your computer’s hard drive. It blocks your system from starting up until you pay a ransom amount.
It goes deep into your computer. It targets a crucial part that starts up your system. When infected, your computer won’t even start. Petya and NotPetya are examples.
Examples of MBR Ransomware
- Petya/NotPetya: Disguised as ransomware, it aimed to cause chaos by destroying data.
- GoldenEye/Petya/NotPetya: It involves an infected MBR and demands payment for decryption.
Prevention
- Install trustworthy antivirus and anti-malware software.
- Regularly make backups of important data on an external hard drive or in cloud storage.
- Enable Secure Boot in your system’s BIOS to prevent unauthorized changes to the MBR.
Response
- Avoid making the payment.
- Seek assistance from cybersecurity experts to recover and remove the ransomware.
- In severe cases, you might need to reinstall your operating system.
Mobile Ransomware

Mobile ransomware is mischievous software that targets your smartphone or tablet, encrypting your data and demanding payment to unlock it.
It’s like the digital hijacking of your device. Once it sneaks in, it locks your screen or encrypts your files. They demand payment to undo the damage. So, protect yourself by staying updated and not clicking on suspicious links. Don’t let these attackers hold your mobile hostage.
Examples of Mobile Ransomware
- Simplocker: It focuses on Android devices, encrypts files, and requests a ransom.
- Charger: Locks your device and asks for payment to unlock it.
Prevention
- To prevent malicious software, download apps from authorized reliable app stores only.
- Keep your device’s operating system and apps updated to patch vulnerabilities.
- Be cautious about granting app permissions that seem unnecessary.
Response
- Disconnect from the internet and remove any suspicious apps.
- Consult cybersecurity experts for guidance on data recovery.
- In some cases, you might need to factory reset your device.
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)

RaaS is a dangerous business involving cybercriminals renting out some kind of ransomware to other attackers.
It is like a criminal marketplace. Cybercriminals are the ones creating ransomware and renting it out as an asset to others. Anyone can rent it from them without being a hacker; simply pay and use it.
This spreads the threat wider. Understand that this criminal service makes ransomware accessible to anyone, making it even more crucial to protect yourself. So, be vigilant against phishing emails and keep your security strong.
Examples of Ransomware-as-a-Service
- Cerber: A notorious RaaS platform that allowed users to distribute the Cerber ransomware.
- Tox: Enabled individuals to create customized ransomware attacks without advanced technical skills.
Prevention
- Employ robust cybersecurity software to block ransomware before it strikes.
- Frequently back up your data to an external source to be able to access your data always.
- Familiarise yourself and your team with the risks of ransomware and safe online practices.
Response
- Disconnect from the network immediately to prevent further spread.
- Use reliable antivirus software to identify and remove the ransomware.
- If possible, restore your data from backups.
Petya Ransomware

Petya is malicious software that infects computers, making your files inaccessible by encrypting them and demanding payment for decryption.
Failure to pay might result in your files remaining inaccessible or exposing your data that anyone can leverage against you. Petya is distributed via email attachments or compromised websites. To protect yourself from it, avoid clicking on suspicious links.
Examples of Petya Ransomware
- Petya/NotPetya: Spread rapidly in 2017, it caused massive disruptions to businesses worldwide.
- GoldenEye/Petya/NotPetya: This Petya variant encrypted files and demanded ransom for their release.
Prevention
- Make sure to consistently update your operating system and applications
- Avoid opening attachments or clicking links from unknown sources.
- Regularly make copies of your data onto an external storage device that isn’t linked to your network.
Response
- Don’t pay the ransom, as there’s no assurance of file recovery.
- Isolate the infected device from the network to prevent further spread.
- Consult cybersecurity experts for advice on recovery and removal.
Common Targets of Ransomware Attacks

Here are five common targets of ransomware attacks that you should be aware of:
- Individuals: Cybercriminals aim at individuals using phishing emails or malicious downloads to encrypt personal files.
- Businesses: Small to large businesses are often targeted due to potential financial gains. Attackers may disrupt operations or steal sensitive data.
- Hospitals and healthcare institutions: Ransomware can paralyze healthcare systems, affecting patient care and demanding ransoms for data recovery.
- Educational institutions: Schools and universities house valuable data and often have vulnerabilities, making them attractive targets.
- Government Agencies: Attackers may exploit government systems, potentially compromising sensitive information and disrupting services.
FAQs
Answer: Common signs of a ransomware infection include sudden file encryption, ransom notes demanding payment, and a locked computer screen. If you notice these signs, disconnect from the internet, don’t pay the ransom, and seek professional help.
Answer: To safeguard your computer and data from ransomware attacks, regularly backup your files, keep your software updated, and be cautious with email attachments and links. Install reliable antivirus software, use strong passwords, and explore more about online threats.
Answer: Yes, law enforcement agencies can track down ransomware attackers. They collaborate with cybersecurity experts and use digital forensics to trace the origin of attacks. However, it’s not always easy due to the use of anonymizing tools and cryptocurrency payments that make tracking more challenging.
Answer: It’s advisable to avoid paying the ransom since there is no assurance of data recovery, and it can also encourage further attacks. Explore other options like restoring from backups or seeking professional help to remove the ransomware and recover your files.
Conclusion
Understanding ransomware and its potential risks is crucial for your digital security. By staying informed about different types of ransomware along with their methods and targets, you’re better equipped to take preventive measures.
Even if you fall victim to an attack, remember not to pay the ransom, isolate the infected device, and seek professional assistance.
To minimize the risk of falling victim to ransomware and safeguard your important data and devices, it is crucial to implement these recommended practices. By remaining vigilant and proactive, you can effectively protect your digital environment from constantly evolving threats.
You may also explore the cyber attack simulation tools to improve security.

