Google controls 92% of the search engine market share globally. It processes billions of queries every day, to be precise, 8.5 billion searches per day.
That’s 99,000 searches per second! 🤯
So, as an SEO specialist or a content marketer, it is crucial for you to dig down this huge pile of search queries and find the ones relevant to your business and audience.
Not when you have the amazing Google search operators.
I use Google search operators to find relevant queries and filter out unnecessary search results. Google search operators are advanced commands and characters for Google Search to show you exactly what you want and nothing else.
This Google advanced search method has helped me trim down my research time and analyze my competitor’s content with ease. In many cases, these Google search commands have helped me find underserved topics as well.
So, let’s explore the Google search operators list that every SEO specialist and content marketer must know.
If you do blogging as a side hustle, this list can help you immensely to find some darn good low-competition topics for a beginner website.
Search Operators Rules
There are two main rules to follow when using Google search operators. Otherwise, you won’t get the results you want.
- Correct Punctuation: If you do not use the correct punctuation mark, Google will usually ignore the operator and not show the expected results.
- Avoid Spaces: Do not use spaces before or after an operator. For example, site:geekflare.com will work, but site: geekflare.com won’t.
These search operators are also alternatively known as Dorks and are used for Google Dorking. So, you need to be careful with the information you find with these operators; do not misuse it, or you can land in legal trouble.
However, the Google search operators I will share today mainly focus on researching your competitor for SEO and marketing purposes. I have also explained some use cases that can help you improve your marketing efforts easily.
Google Search Operators List
Knowing how to craft perfect Google search queries can greatly impact your efficiency and overall research process. Search operators can be broadly classified into two categories: Reliable and Unreliable.
➡️ Reliable: Gives the expected results.
➡️ Unreliable: The search results are hit-and-miss. You might get the expected results, or you won’t.
These Google search operators will also work on Google Chrome alternatives, such as DuckDuckGo, Bing, Yahoo, Brave, and more.
Reliable Google Search Operators
-inurl:
- Excludes results with a particular search term in the URL.
- Example: inurl:geekflare.com -inurl:tools
cache:
- Fetches the most recent cache of a webpage.
- Example: cache:sparkian.com
allintext/intext:
- Fetches results with the specific or all search terms anywhere on the page.
- Example: allintext:dorking, intext:dorking
site:
- Fetches results from a specific website.
- Example: site:geekflare.com
filetype:
- Fetches particular types of files (e.g., PDF, XLS, etc.).
- Example: site:semrush.com filetype:pdf
intitle/allititle:
- Show pages with the specific or all search terms in the page’s title.
- Example: site:geekflare.com intitle:cybersecurity, site:geekflare.com allintitle:cybersecurity data
*
- A wildcard. It will match with any word or phrase. It must be combined with some other operator.
- Example: site:*geekflare.com
info:
- Fetches all the available information about a specific page or website.
- Example: info:geekflare.com
“”
- Fetches results that exactly mention a particular word or phrase.
- Example: “cristiano ronaldo news”
|/OR
- Fetches results related to X or Y.
- Example: manchester united | liverpool, manchester united OR liverpool
AND
- Fetches results related to X and Y.
- Example: google ads AND facebook ads
in
- Converts one unit to another.
- Example: GBP 1000 in AED
()
- Groups multiple search terms to show results.
- Example: (seo OR ppc) site:geekflare.com
source:
- Search for results from a particular source in Google News.
- Example: source:crunchbase geekflare
before/after:
- Search for results from before/after a particular date.
- Example: geekflare.com before:2020-06-18, geekflare.com after:2020-06-18
🔔 Note: For before and after operators, if you’re using the full dates, the search has to be done in the year/month/day format.
Unreliable Google Search Operators
If you don’t care about the hit-and-miss aspect of some Google Search Operators, check out a few of the not-so-trustworthy operators below!
inanchor/allinanchor:
- Search for pages with backlinks containing specific/multiple words in anchor text.
- Example: inanchor:seo marketing, allinanchor:seo marketing
around(X)
- Returns results where the two terms/phrases are within (X) words of each other.
- Example: seo AROUND(2) content
loc/location:
- Shows search results from a specific location.
- Example: location:new_york dominos_pizza
daterange:
- Fetches results from a particular date range.
- Example: elden ring daterange:20278-22278
#…#
- Search within a range of numbers.
- Example: oneplus phones $150..$200
- Look for websites related to the defined domain.
- Example: related:geekflare.com
🔔 Note: For the daterange operator, Julian date format is followed. The year is followed by the number of days since the beginning of the year.
Powerful Google Search Operator Use Cases for SEOs & Marketers
So, now that you know all the reliable and unreliable Google search operators, you need to understand how to use them. If you do not want to remember these operators, you can even use the Google Advanced Search page for your research.
However, I recommend using the Google search operators, as typing a search query directly with them is less complicated.
Some operators are not very beneficial in themselves, but combining them with others can open up a wealth of information for you.
So, let’s see how SEOs and marketers can use these operators and trim their research time by fetching exactly the Google results they want.
#1. Find Vulnerable/Unintentionally Indexed Pages
Many hackers exploit these operators and try to find data or documents accidentally uploaded online. If any confidential business document is accidentally exposed, a black hat hacker can find it and use it against you.
For example, a PDF containing database credentials or an Excel sheet with login details of your employees. A hacker can get unauthorized access to your system if they find these details.
Even your competitors can do this to get an edge over you.
Operator String: site:[website] filetype:[pdf/xls/html/etc.]
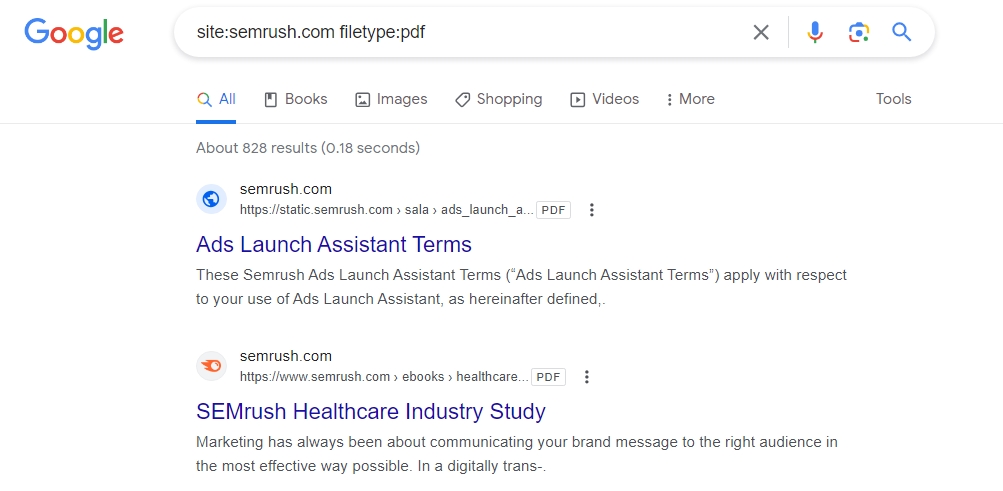
Now, you can check which documents are not supposed to be on the internet and de-index them by adding the URLs to your robots.txt file. Just add an x-robots noindex tag to solve this.
#2. Find What Kind of Posts Your Competitor Writes
With the combination of correct operators, you can steal your competitor’s content strategy. You can check what content they mostly write and then replicate it.
For example, if I search for site:pcmag.com, I can quickly see that they write many product review posts and technology-focused content.
It’s something that Geekflare does, too.
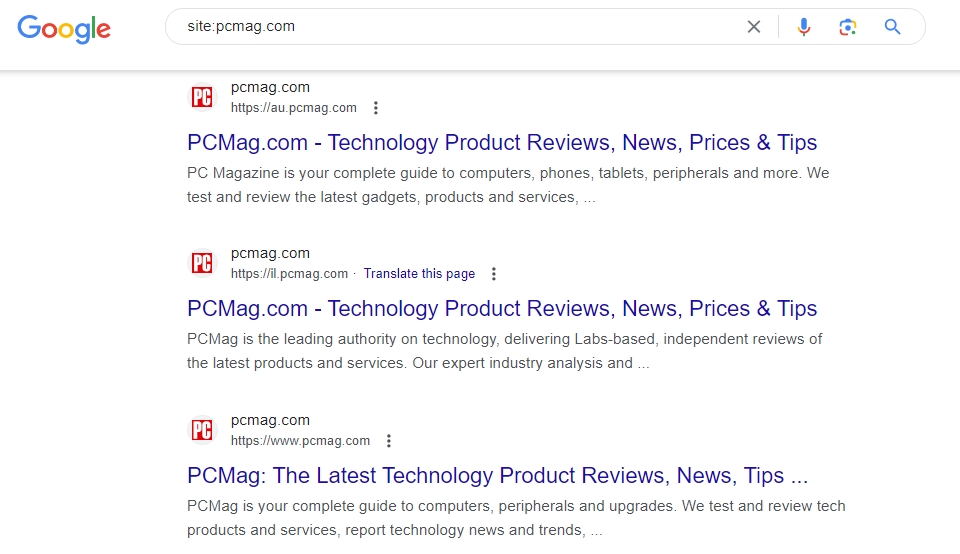
All content marketers and SEOs know that the best keywords to target are informational keywords like “how to…”, “what is…”, etc.
So, let’s say I want to see how many how-to or what-is posts PCMag has; I can quickly do so.
Operator String: site:[website] intitle:[ “how to” OR “what is”]

Furthermore, you can verify these URLs for their traffic using a competition research tool like Semrush, Ahrefs, Mangools, or more. Prioritize the search terms that get a lot of traffic.
You don’t want to target queries that don’t get traffic, right?
#3. Build Backlinks with Guest Posts/Sponsored Posts
Writing guest posts on a high domain authority website and securing Dofollow backlinks can be a great way to boost your rankings on Google. Your competitors are already doing it, why won’t you?
Operator String: [keyword] intitle: “write for us” inurl:write-for-us
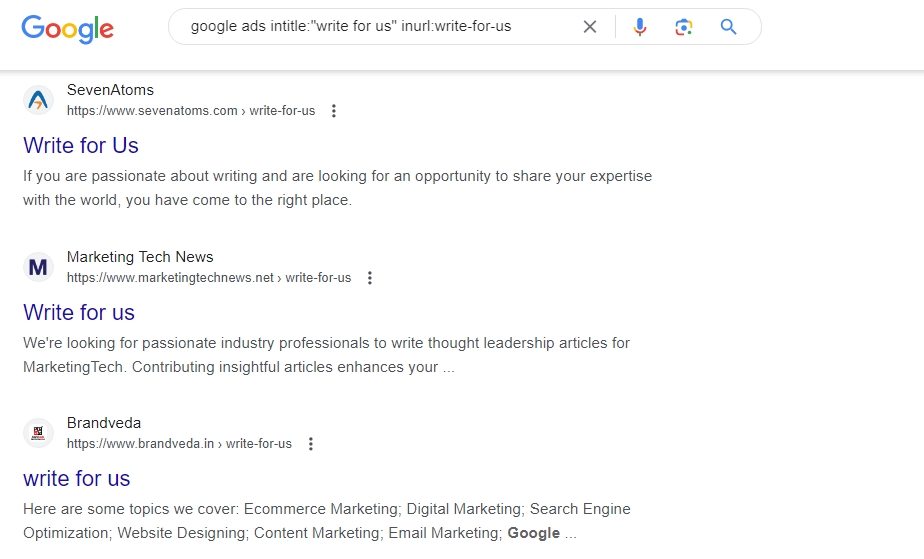
Here, I want to build backlinks for a Geekflare post on Google Ads, so I search for websites that talk about Google Ads and accept guest posts too.
Also Read: How To Become A Google Ads Specialist: Online Courses You Should Know About
Now, I can simply email these sites and ask them if I can submit a guest post.
#4. Discover Interlinking Opportunities
Interlinking is one of the biggest parameters for page ranking. It helps pass on that sweet SEO link juice from a top-ranking page to a low-ranking one, eventually boosting its ranking.
Using Google search operators, you can easily find pages to interlink. Let’s say I have a new post on Big Data, and I want to scan through old Geekflare posts to see contextual interlinking opportunities.
Operator String: site:geekflare.com intext:” big data”
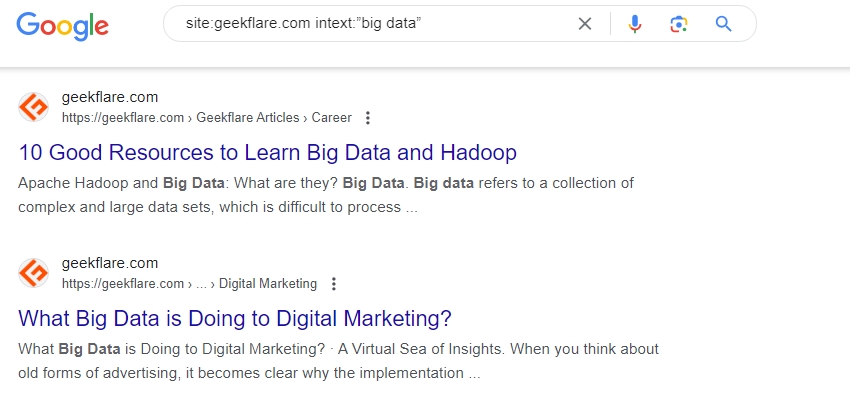
This way, I can easily find old posts and link my new post about Big Data, creating contextual interlinking opportunities.
#5. Find Relevant Listicles That Don’t Mention Your Brand
Let’s say you have a Shopify-based business. You have a subscription app for Shopify, like Recurpay. The app helps Shopify sellers create product bundles and sell them as subscriptions.
Using the right Google search operators, you can find high-authority websites that write listicles on Shopify-related topics. And then, check if these listicles mention your app. If they don’t, request them to include your app in the list.
Operator String: best [topics/benefits related to your brand] -” [brand name]”
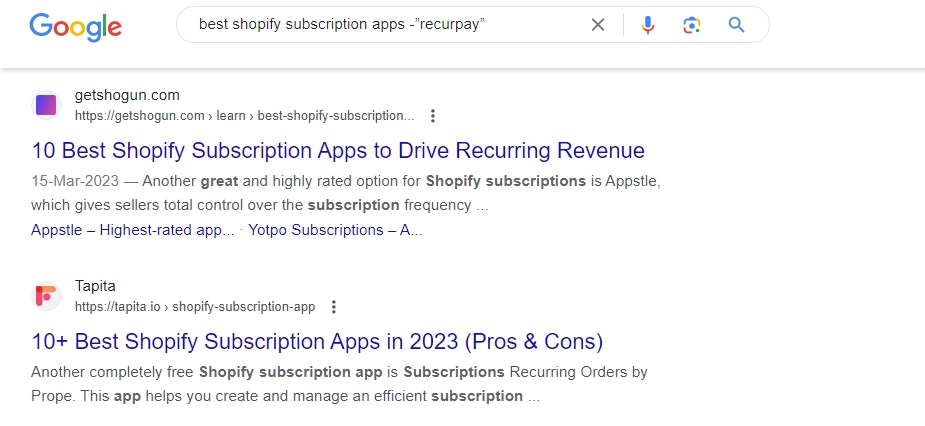
These are some really good top-ranking websites, and featuring your product in their listicles can help you gain organic traffic and increase sales.
#6. Find Relevant Community Discussion Topics and Forums
Forum websites like Reddit, Quora, IGN, and more are great platforms to promote your brand and interact with the direct users of your product.
You can quickly find discussions and questions being asked in your niche and then join in.
Operator String: site:website.com intitle:keyword
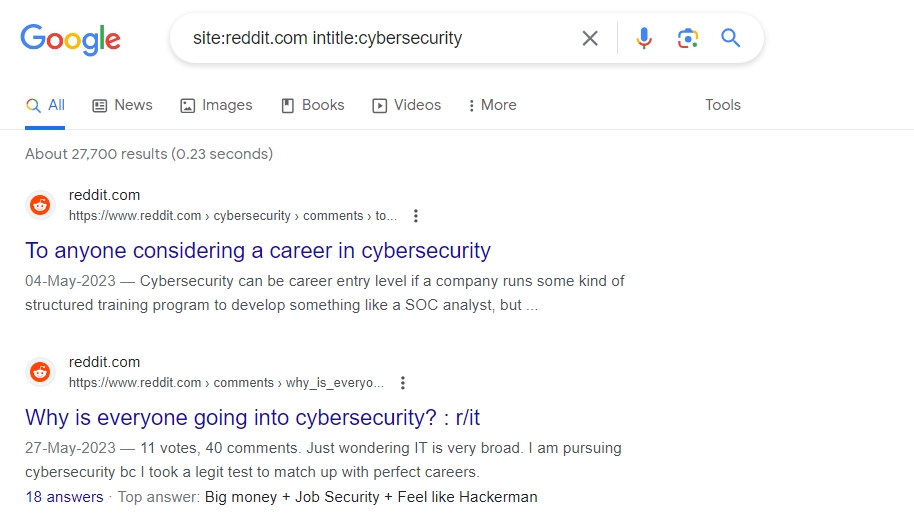
You can engage in these conversations from your branded profile and offer a solution. If the user wants more details, you can even link to your website, article, or video.
However, I recommend not over-promoting your brand as the community moderators might consider it spamming and ban your account.
#7. Discover Non-HTTPS Indexed Pages
HTTP is a network protocol that encrypts the data exchanged between a user’s browser and a website’s server and keeps it safe. Hence, every website must have an SSL certificate.
With a couple of operators, you can find non-HTTPS pages on your site that have been indexed, advertently or inadvertently.
Operator String: site:[website.com] -inurl:https
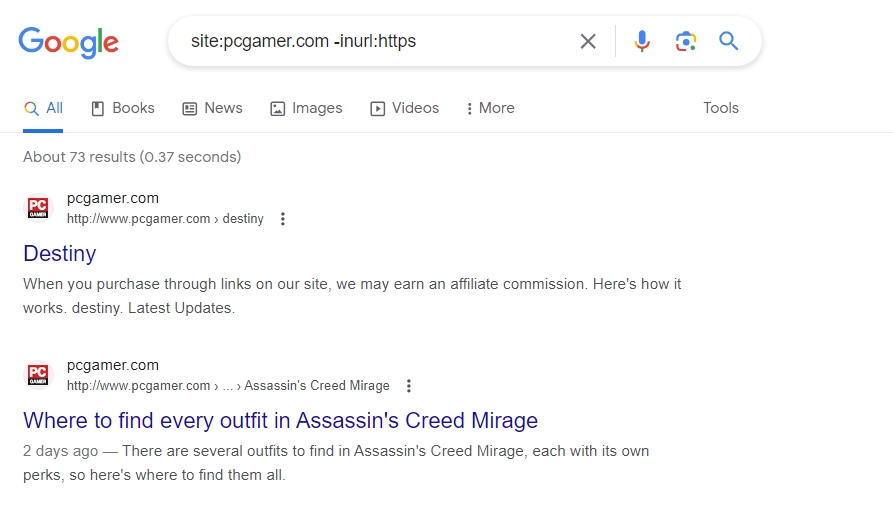
After using this Operator String, you should always double-check the pages in search results. Because, sometimes, when you visit the actual page, you will land on the HTTPS version. The web page might already be redirected to the HTTPS version.
If you check your own website and find some indexed HTTP pages, you visit the actual pages, and still they are not secure, then check your SSL certificate.
#8. Check for Duplicate Content/Plagiarism
You can use a plagiarism checker tool to check for duplicate content on your website. However, if you do not have the budget, you can use this simple operator to find duplicate content.
Operator String: “duplicate content you want to check.”
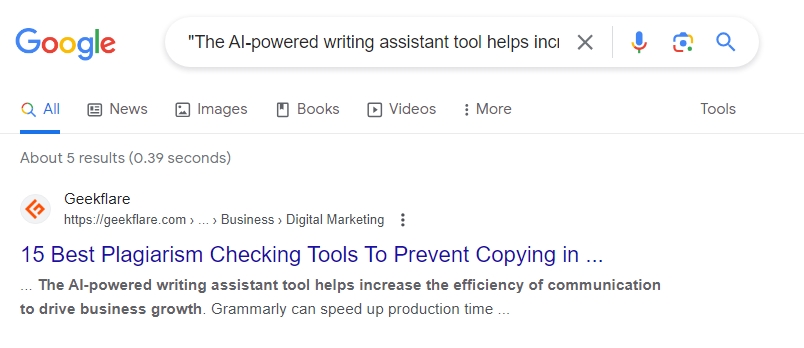
Who knows, you might find some websites stealing and republishing your content without permission or attribution!
#9. Find Marketing Tools With Free Trials
Using Google search operators, you can easily find SaaS tools or any tools that have a free trial. Just search for the primary keyword about the tool you’re looking for and combine it with some other operators.
Operator String: “keyword” intext:free trial OR inurl:free trial

If you’re looking for a specific tool and want to check if it has a free trial plan – just replace the tool name with the keyword in the operator string. For example: “semrush” intext:free trial OR inurl:free trial
#10. Find Social Profiles for Outreach
Reaching people via social media profiles is a great way to build business relationships and land eventual clients. You just know their name? That’s it. That’s all we need.
Operator String: [name] site:twitter.com | site:facebook.com | site:linkedin.com

You can then contact the people directly via social media and build a professional repertoire. You can add even more social media sites like Instagram, TikTok, and more.
#11. Search Relevant Images for Your Posts
You don’t even need a Google search operator for this. You can find relevant images for your social media or blog posts using Google’s Advanced Image Search page.

Add the details and do the Google advanced search. Google will give you all the relevant images that match your search criteria.
Final Thoughts
Google search operators are super powerful if correctly used. You just need a handful of operators to make your research process quicker and more efficient.
Not all of them are useful by themselves, so you need to combine them with other operators like we used a combination of operators to find free trials of email marketing tools.
I mostly use site, intitle, inurl, -, and ” ” for my content research, and I recommend that you do the same.
Explore the Google search operators list and experiment with them to get the exact search results you want.

