Learn the basics of Cybersecurity and get to know tools to find vulnerabilities, protect website, mitigate application security risks, secure your IT infrastructure, and protect your business reputation.
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the process and techniques involved in protecting sensitive data, computer systems, networks, and software applications from cyberattacks. The cyberattacks are general terminology that covers many topics, and some popular are:
- Tampering systems and data stored within
- Exploitation of resources
- Unauthorized access to the targeted system and accessing sensitive information
- Disrupting the normal functioning of the business and its processes
- Using ransomware attacks to encrypt data and extort money from victims
The attacks are now becoming more innovative and sophisticated, which can disrupt the security and hacking systems. So it’s very challenging for every business and security analyst to overcome this challenge and fight back with these attacks.
To understand the need for Cybersecurity measures and their practices, let’s take a quick look at the types of threats and attacks.

Ransomware
Ransomware is a file encryption software program that uses a unique, robust encryption algorithm to encrypt the files on the target system. The authors of the Ransomware threat generate a unique decryption key for each of its victims and save it on a remote server. Thus, users cannot access their files by any application.
The ransomware authors take advantage of this and demand a considerable ransom amount from the victims to provide the decryption code or decrypt the data. But such attacks have no guarantee of recovery of data even after paying the ransom.
Botnets Attacks
Botnets were initially designed to carry out specific tasks within a group. It is defined as a network or group of devices connected with the same network to execute a task. But this is now being used by bad actors and hackers that attempt to access the network and inject any malicious code or malware to disrupt its working. Some botnet attacks include:
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks
- Spreading spam emails
- Stealing of confidential data
Botnets attacks are generally carried out against large-scale businesses and organizations due to their huge data access. Through this attack, the hackers can control many devices and compromise them for their evil motives.
Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering is now a common tactic used by cybercriminals to gather user’s sensitive information. It may trick you by displaying attractive advertisements, prizes, huge offers, and asking you to feed your personal and bank account details. All the information you enter there is cloned and used for financial fraud, identity fraud, and so.
It is worth saying about the ZEUS virus that is active since 2007 and is being used as a social engineering attack method to steal the victims’ banking details. Along with financial losses, Social engineering attacks can download other destructive threats to the concerned system.
Cryptocurrency Hijacking
Cryptocurrency hijacking is the new addition to this cyber world. As digital currency and mining are becoming popular, so it is among cybercriminals. They have found their evil benefit to cryptocurrency mining, which involves complex computing to mine virtual currency like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Monero, Litecoin, etc.
Cryptocurrency investors and traders are the soft targets for this attack.
Cryptocurrency hijacking is also known as “Cryptojacking”. It is a program designed to inject mining codes silently into the system. Thus, the hacker silently uses the CPU, GPU, and power resources of the attacked system to mine for the cryptocurrency.
Phishing
Phishing is a fraudulent action of sending spam emails by imitating to be from any legitimate source. Such mails have a strong subject line with attachments like an invoice, job offers, big offers from reputable shipping services, or any important mail from higher officials of the company.
The phishing scam attacks are the most common cyberattacks that aim to steal sensitive data like login credentials, credit card numbers, bank account information, etc. To avoid this, you should learn more about phishing email campaigns and their preventive measures. One can also use email filtering technologies to avoid this attack.
Malware
Malware is a broad term referring to all malicious programs that can harm a computer system or network. It includes viruses, worms, ransomware, spyware, and trojanware that can steal data, corrupt files, disrupt operations, or even take control of a system with malicious intent.
Supply Chain Attacks
Supply chain attacks target less-protected third-party vendors or suppliers of a company to gain access to that company’s network. This attack leverages the trust between business partners, and hence, it is difficult to defend.
Zero-day Attacks
These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in software that the software vendor is unaware of. Since no patch exists to fix the vulnerability, these attacks are highly effective and can cause significant damage before a solution is developed. Zero-day attacks are often used by sophisticated attackers targeting high-value targets like government agencies or critical infrastructure.
DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks overwhelm a website or network with a flood of traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users. Hackers get control of a network of compromised computers, which bombards the target with junk requests to achieve this attack. These disrupt online services, causing financial losses and reputational damage.
IoT Attacks
IoT attacks target IoT-connected devices such as smart home appliances, wearables, or industrial control systems. Attackers can exploit insecure IoT devices to steal data, disrupt operations, or even launch further attacks on a wider network.
Trojanware
Trojanware is a type of malware disguised as legitimate software that tricks users into installing them. After installation, it gets unauthorized access to the system to easily steal data, disrupt system operations, or even install other malware.
Eavesdropping
Eavesdropping involves secretly listening to phone calls or intercepting e-communications, such as emails or DMs. Eavesdroppers use various techniques to capture confidential information that they utilize for identity theft or other fraudulent activities.
The key concept of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is a very broad term but is based on three fundamental concepts known as “The CIA Triad“.
It consists of Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. This model is designed to guide the organization with the policies of Cybersecurity in the realm of Information security.
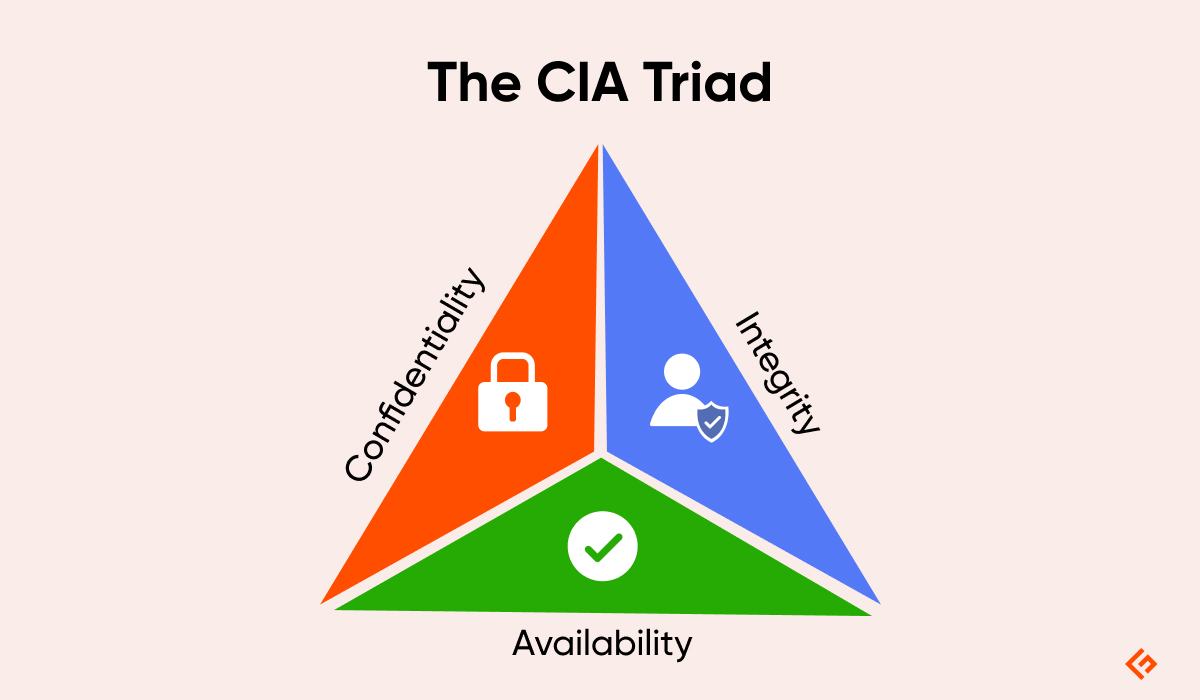
Confidentiality
It defines the rules that limit access to information. Confidentiality takes on the measures to restrict sensitive information from being accessed by cyberattackers and hackers.
In an organization, people are allowed or denied access to information according to its category by authorizing the right persons in a department. They are also given proper training about the sharing of information and securing their accounts with strong passwords.
They can change the way data is handled within an organization to ensure data protection. There are various ways to ensure confidentiality, like two-factor authentication, data encryption, data classification, biometric verification, and security tokens.
Integrity
This assures that the data is consistent, accurate, and trustworthy over its period. It means that the data within the transit should not be changed, altered, deleted, or illegally being accessed.
Proper measures should be taken in an organization to ensure its safety. File permissions and user access control are the measures controlling the data breach. Furthermore, tools and technologies should be implemented to detect any change or a breach in the data. Various organizations use a checksum and even cryptographic checksum to verify the integrity of data.
To cope with data loss or accidental deletion, or even cyberattacks, regular backups should be there. Cloud backups are now the most trusted solution for this.
Availability
Availability in terms of all necessary components like hardware, software, networks, devices, and security equipment should be maintained and upgraded. This will ensure the smooth functioning and access of Data without any disruption. Also, providing constant communication between the components through providing enough bandwidth.
It also involves opting for extra security equipment in case of any disaster or bottlenecks. Utilities like firewalls, disaster recovery plans, proxy servers, and a proper backup solution should ensure to cope with DoS and DDoS attacks.
What is Vulnerability Management?
Vulnerability management is the process that identifies, prioritizes, and addresses flaws in computer systems and software. Hackers can easily abuse such weaknesses or bottlenecks in security to gain unauthorized access, steal personal and sensitive data, or disrupt application operations. Vulnerability management constantly searches for these vulnerabilities, assesses their severity, and patches or fixes them. Thus, businesses can protect themselves from cyberattacks. All technology-based organizations need this to proactively prevent security incidents.
How Does Vulnerability Management Work
The vulnerability management process begins with identifying the vulnerabilities of an organization’s IT or software. Tools perform automated scans to compare systems to the databases of known weaknesses. After some flaws are identified, the severity assessment of each vulnerability takes place.
The factors considered during the assessment are the likelihood of the weakness being targeted, ease of exploitation, and its ability to cause damage. After the assessment, organizations set their priorities and create a plan to address the risks. The plan usually involves patching software, implementing security configurations, and isolating vulnerable systems. Once the actions are done successfully, the whole process starts from the beginning.
Importance of Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management offers a proactive approach to reduce attack risk, improve efficiency, and ensure compliance.
Proactive Defense: Organizations that use vulnerability management can identify and address their system weaknesses before attackers exploit them. Thus, the proactive approach reduces the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches.
Reduced Attack Surface: It allows businesses to shrink the potential entry points for attackers. As a result, attackers find it difficult to get hold of the system.
Prioritization and Efficiency: By assessing the severity of the weaknesses, vulnerability management tools let organizations prioritize which ones to fix first. It enables companies to focus on the most critical risks first, leading to optimized security efforts.
Improved Regulatory Compliance: Many data privacy regulations require organizations to have a vulnerability management program. Businesses need it to ensure regulatory compliance to avoid potential fines and legal issues.
Reduced Costs: Data breach events are often incredibly expensive because of financial penalties, data recovery costs, customer churn, and reputational damage. Effective vulnerability management helps companies prevent these costly incidents.
Benefits of Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management offers various benefits, such as a stronger security posture, streamlined processes, and better decision-making.
Enhanced Security Posture: The vulnerability management method offers a continuous identification, assessment, and remediation loop. This ongoing process strengthens the security posture of the organization.
Streamlined Patch Management: Vulnerability management tools often integrate with patching systems, allowing for a more efficient patching process. You can prioritize vulnerabilities, automate patch deployment for low-risk systems, and track progress, saving valuable time and resources.
Improved Security Team Efficiency: Since vulnerability management involves task automation and prioritizes vulnerability, the security team can focus on more strategic initiatives. It frees them up to work with complex threats and proactive threat hunting, where they can fully utilize their expertise.
Better Decision-Making: Vulnerability management tools provide valuable insights into the organizational security landscape. Security leaders can make informed decisions using resource allocation, security investments, and overall security strategy.
Demonstrated Security Maturity: A robust vulnerability management program shows a business’s proactive commitment to security practices. It attracts clients and partners who value strong security posture and data protection.
What is Monitoring?
Monitoring is the security approach of constantly watching the IT systems of an organization. It looks for suspicious activity in network traffic, system logs, and user behavior that might indicate a cyberattack. Once it identifies any anomaly, users can stop the threats before they cause any damage. There are two types of monitoring: network monitoring to observe the data flow and endpoint monitoring for devices like laptops and servers.
How Does Monitoring Work
Monitoring is like having a dashboard for the system to constantly collect data, such as server performance or website traffic. Monitoring software plays a key role in monitoring security by automatically collecting data and checking it against predefined criteria. Whenever it detects something abnormal, it alerts the responsible person of a potential issue. Hence, organizations can take proactive intervention before the problems impact the users or become a severe issue. Continuous monitoring is essential for smooth organizational operation and data-driven decisions.
Importance of Monitoring
Monitoring is important for early threat detection and reduced downtime and cost.
Early Threat Detection: The continuous monitoring identifies real-time suspicious activities and potential security incidents. This enables businesses to respond swiftly with mitigation strategies before threats cause significant damage.
Improved Incident Response: Using effective monitoring, organizations get valuable data and insights during a security incident. Thus, they can pinpoint the origin of the attack, understand its scope, and take quick actions to contain the damage.
Enhanced Threat Detection: IT security teams utilize monitoring data to proactively identify hidden threats within the systems. Hence, monitoring helps locate sophisticated attacks that might bypass traditional security techniques.
Reduced Downtime and Costs: Monitoring can quickly detect and respond to security incidents, resulting in minimized downtime. In such cases, organizations have to bear with less operational costs and loss of productivity.
Benefits of Monitoring
Monitoring benefits businesses by streamlining security operations, improving security posture, and compliance with regulations.
Streamlined Security Operations: Security monitoring tools automate tasks and processes like log collection, anomaly detection, and initial alert assessment. Hence, security analysts and IT teams focus on more strategic initiatives, such as in-depth threat investigation and response.
Compliance with Regulations: System monitoring for security breaches and suspicious activity is mandatory according to many data privacy regulations. Monitoring helps organizations comply with these regulations and avoid any legal repercussions.
Improved Security Posture: Through constant monitoring, businesses get a deeper understanding of their security vulnerabilities and scope of exploitation. They can leverage this knowledge to strengthen the security posture by prioritizing vulnerabilities and implementing security measures.
Proven Security Maturity: An organization with a powerful monitoring program is committed to securing user data and confidential information. It attracts clients and partners who prioritize a mature security culture and continuous system monitoring.
What is Web Application Security?
Web application security (Web AppSec) refers to the protection of websites, web apps, and online services from cyberattacks that attempt to exploit the weaknesses in the code. Through exploitation, hackers try to steal sensitive data, disrupt regular operations, or cause damage to the service. Web AppSec involves secure coding practices, security testing, and fixing weaknesses that developers perform during the lifecycle of the web app.
How Does Web Application Security Work
Web application security involves building a multi-layered defense mechanism to protect the web application throughout its lifecycle. Developers need to follow secure coding practices such as user input validation and encryption for sensitive data to avoid vulnerabilities from the beginning of development.
Throughout the remaining process, developers integrate security. Security is also integrated throughout the development process after identifying weaknesses with testing tools scanning. After deployment, web app firewalls block suspicious attempts, and secure authentication methods stop hackers from stealing login credentials. Combining all these strategies, web application security creates a strong defense against cyber threats.
Importance of Web Application Security
Web application security is important for protecting data, ensuring business continuity, and safeguarding your reputation.
Data Security: Web applications manage sensitive information such as login credentials, personal details, and financial records. A security breach can expose this data to hackers, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational damage. Implementing a strong security plan helps companies safeguard their web applications.
Business Continuity: When attackers disrupt web applications, outages will be hindering regular business operations. Web application security measures ensure uninterrupted availability and functionality of the application.
Compliance With Regulations: There are many local and global regulations about user data management for organizations. If companies fail to comply with these, there will be legal repercussions, such as fines and penalties. Web application security meets these compliance standards.
Reputation Management: Web application security prevents data breaches and security incidents that can damage an organization’s reputation. It also demonstrates an organization’s commitment to protecting user data and privacy.
Mitigation of Financial Losses: A data breach can lead to expensive data recovery, financial penalties, reputational damage, and financial loss from outages. Robust web application security minimizes the risk of cyberattacks and these associated costs.
Benefits of Web Application Security
Web application security goes beyond just protection; it provides a range of benefits, from user trust and development efficiency to cost savings and a stronger brand image.
Enhanced User Experience: When a web application is secure, it gains user trust and confidence because they know that their information is protected. When users engage with the application without worries, their experience is enhanced to a great extent.
Improved Development Efficiency: Secure coding practices and early vulnerability detection streamline the development process. As fixing vulnerabilities early in the product lifecycle is easier and faster than post-deployment, the development workflow becomes more optimized.
Reduced Expenses: When a security breach happens to a web application, the company must invest significant money and resources to address the issue and restore functionality. With a proactive web application security approach, businesses can minimize the chances of cyberattacks and, thus, avoid costly disruptions.
Early Threat Detection and Response: Web AppSec tools and monitoring techniques identify and alert developers to potential threats in real-time. Hence, organizations get more time to mitigate the vulnerabilities before the attackers exploit the web applications.
Stronger Brand Image: Businesses that take data security seriously are committed to user privacy and security. This responsible practice enhances their brand image and establishes them as a trustworthy organization.
Improved Overall Security Posture: Web application security is crucial to a company’s overall cybersecurity strategy. By securing web applications, organizations strengthen their entire security infrastructure.
What is Network Security?
Network security is the defense system that protects a network and its data. This approach safeguards the network from unauthorized access, disruptions, misuse, alteration, or destruction. It consists of various tools, processes, and best practices to create a powerful shield around the network.
How Does Network Security Work
Network security employs a multi-layer defense system to protect the network and its data flow. The first line of defense is firewalls that filter incoming and outgoing traffic based on configured security rules. Encryption makes data unintelligible to anyone without the decryption key. The authentication method confirms the identity of a user, while authorization determines their access level within the network. Network security software constantly screens data to fight malware and other threats. Together, all these network security methods create a flawless defense against ever-evolving cyber threats.
Importance of Network Security
Network security is important for the protection of sensitive data, improvement of system performance, maintenance of user privacy, protection against legal consequences, and more.
Protection of Sensitive Data: Networks often store sensitive data, such as financial records, user data, and intellectual property. Network security is essential to protect this data from unauthorized access, theft, or leakage.
Maintenance of User Privacy: The network also stores personal information like login credentials, browsing history, and online communications. With network security, users can prevent unauthorized access to such information.
System Performance Improvement: Malicious software and unauthorized usage hamper network performance. Network security measures successfully prevent these issues, leading to optimal network speed and stability.
Cyberwarfare Prevention: Network security is crucial for national security, as cyberattacks disrupt essential services. Governments can deter cyberattacks by protecting critical infrastructure networks with network security.
Protection Against Legal Consequences: The biggest importance of network security lies in its ability to protect businesses against legal consequences. Hackers can steal customer data by breaching the network, affecting numerous people. Businesses face hefty fines as they fail to safeguard the data. For this reason, network security is vital for businesses.
Benefits of Network Security
The benefits of network security include financial security, protection from data breaches, reduced IT costs, compliance and regulation, and more.
Protection from Data Breaches: Network security systems, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption, function as a shield against unauthorized data access. It prevents hackers and even insiders from stealing or compromising sensitive information.
Enhanced Financial Security: Cybercriminals aim to steal financial data or extort money through ransomware attacks. Network security safeguards sensitive financial data such as credit card credentials and bank account numbers.
Improved User Confidence: Strong network security ensures complete protection of personal information. This benefits eCommerce companies, financial organizations, and businesses handling sensitive user data. It spreads a sense of trust and confidence among the users and encourages them to engage with these reliable online services.
Reduced IT Costs: Network security prevents malware infections and data breaches. It saves the organization money they would have spent otherwise on data recovery approaches and security management resources.
Boosted Productivity: Network security guarantees a secure environment free from malware and disruptions. It enables users to focus on their tasks without any worry. As a result, organizations get increased productivity and improved efficiency.
Compliance with Regulations: Network security helps businesses comply with regulations essential for their industries. Thus, companies can avoid penalties and other legal repercussions associated with data breaches.
What is Data Recovery?
Data recovery is the process of getting back information from a storage device. This approach is used when data is deleted, corrupted, damaged, or formatted. While it is not directly a cybersecurity measure, data recovery is vital to an incident response plan following a cyberattack through mitigation, investigation, and improved preparedness.
How Does Data Recovery Work
The data recovery process involves two major techniques for information retrieval. For hardware problems or any physical damage to storage devices, data recovery demands physical intervention. For example, in the case of a failed hard drive or a corrupt memory card, data recovery specialists use equipment and clean room environments to clean damaged components, bypass faulty controllers, or use functional parts from another device to recover the information.
For logical issues like accidental deletion or file corruption, software solutions tackle the situation. To find a lost file, data recovery software analyzes the file system structure and searches for recoverable data fragments. Thus, it joins these fragments to rebuild the original file.
While the data recovery process usually follows one of these methods, its success rate depends on the gravity of the issue. Software-based data recovery is usually more successful for recently deleted files, while physical recovery gets more complex and expensive with extensive damage. In both cases, users can increase the chances of successful data recovery by minimizing further usage of the storage device after data loss.
Importance of Data Recovery
The importance of data recovery is to ensure business continuity during the crisis, protect against malware, and peace of mind.
Restores Crucial Data: critical business documents and creative work are all susceptible to data loss due to accidental deletion, hardware failure, or cyberattacks. Data recovery restores data and information that are impossible to recreate in most cases.
Ensures Business Continuity: Customer records and financial data are essential for daily business operations. Loss of such data leads to operational downtime and financial setbacks. A successful data recovery minimizes disruption and quickly gets the operations back on track.
Protects Against Ransomware: Ransomware attackers often threaten to permanently erase data unless a ransom is paid. If businesses have a proper data recovery plan, they can restore their data without succumbing to extortion.
Comparatively Cost-Effective: To recreate lost data from scratch is undoubtedly a time-consuming and expensive process, especially for complex projects. Compared to that, data recovery is a more cost-effective solution that lets companies regain access to their information.
Offers Peace of Mind: Data loss is a stressful event because it can lead to privacy concerns, financial loss, and feelings of helplessness. When users know that they have a data recovery plan in place, they get peace of mind.
Benefits of Data Recovery
Data recovery implementation benefits businesses by recovering lost or inaccessible data, complying with local regulations, and mitigating cyber threats.
Data Salvation: The biggest benefit of data recovery is data salvation. It lets users retrieve lost or inaccessible files because of data corruption, data deletion, or data theft.
Regulatory Compliance: Data security regulations of certain industries require businesses to have a data recovery plan in place. Data recovery ensures compliance with these regulations and enables businesses to avoid potential legal repercussions.
Protection Against Security Threats: Data recovery plans shield businesses from security threats and cyberattacks. When users have data backed up for recovery, they can restore files without paying the ransom.
Preserving Memories: Some memoirs are irreplaceable, like vintage family photos of extended family. In case of data loss, data retrieval allows users to retrieve files and images that are impossible to recreate.
Maintaining a Competitive Edge: Data loss costs businesses money, time, productivity, and reputation. When a business has a data recovery plan, it maintains a competitive edge over the competitors.
What is Antivirus?
Antivirus software protects devices and systems from viruses, malware, Trojan, and many more. These malicious elements infect a computer through downloads, email attachments, or even clicks on links. Antivirus software constantly monitors to stop these from entering or using the device. Besides identifying and blocking known threats, it detects suspicious activity.
How Does Antivirus Work
Antivirus software works in two main ways: file and program scanning for suspicious patterns, and behavior monitoring for red flags. Antivirus applications have a large database of known malware signatures or unique identifiers. The antivirus software compares it to these signatures to see if there is a match. In that case, the antivirus program quarantines or removes the malicious file.
Antivirus software monitors the activity happening inside the device to screen if any program is trying to access unauthorized files or using excessive resources. It flags any such suspicious activities for investigation or stops it. In most cases, antivirus software uses these two methods to offer layered defense against evolving online threats.
Importance of Antivirus
The importance of antivirus includes data security, real-time protection from malware, and prohibiting spam emails from reaching your inbox.
Protection from Malware: Antivirus software does not only protect against viruses. It safeguards user devices from malware, such as spyware, ransomware, worms, and trojanware. Malware can steal personal information, corrupt the system, hold the files hostage, and do more harm.
Data Security: Individuals and businesses store crucial data in their systems. Keeping it without any antivirus software means leaving the system vulnerable to all kinds of hackers and cybercriminals. Antivirus software is essential for the security of personal and sensitive information.
Stopping Spam Emails: Many antivirus software offer a spam filter feature that blocks unwanted and potentially dangerous emails from reaching inboxes. Spam emails can contain phishing links and malware to trick users into giving away their personal information. Prohibiting these emails from reaching the user assures additional security.
Real-Time Protection: Antivirus software always runs in the background to monitor the system for threats. Thus, it offers real-time protection against malware and keeps the system free from any infection.
Regular Updates: Antivirus software needs to be updated regularly to be prepared to fight all the latest malware. Most antivirus programs automatically install updates to enrich their databases with the knowledge of the latest threats.
Benefits of Antivirus
Antivirus offers various benefits such as improved system performance, more privacy over information, cost-effectiveness eventually, and more safety while shopping online.
Cost-Effective: There is free and paid antivirus software. No matter which type of program you choose, it will save users money in the long run.
Improves Performance: Any kind of malware and virus infection slows down your computer and significantly hampers the computer’s performance. Antivirus software prevents malware from infecting the computer to keep the system running smoothly. Thus, it has a positive impact on the performance of the antivirus.
Privacy: Different malware infections can steal personal information, financial credentials, and browsing history. Antivirus software blocks these to protect user privacy and keep sensitive information a secret.
Safe Online Shopping: When users have antivirus software installed, they can shop online more confidently. Antivirus software prevents phishing scams and other online threats and keeps financial information and online activities secure.
Parental Control: Some antivirus programs also include parental control features that allow users to manage their children’s internet activities. These applications enable users to block inappropriate websites, monitor online activity, and set time limits for internet usage. Moreover, users do not have to install separate software for parental control.
What is Privacy?
User privacy in cyberspace is a complicated issue. It means controlling the online presence of someone’s personal information, such as name, address, social security number, banking information, browsing history, and online purchases. Maintaining privacy also involves the ability to choose what you want to share with the world.
Privacy encompasses physical privacy, like the prohibition of intrusion in someone’s personal space, and informational privacy, which means the right to control how user data is collected and used. Privacy ensures the autonomy and safety of the user, both online and offline. With technological advancement, privacy has become a more complex concept.
How Does Privacy Work
Privacy in the digital world is an ongoing conversation. It requires a combination of user awareness, responsible data practices by companies, and responsible regulations to enable smooth connection without compromising user privacy.
Data privacy requires vigilance from multiple parties, namely users, organizations, and government agencies. Users should carefully share their personal information and take other security measures like using strong passwords and adjusting privacy settings.
Companies should collect minimal data and be transparent about data storage and data use. They must implement strong security and comply with data privacy regulations around the world. Governments of different countries should have laws and regulations like GDPR that give users more control over their data.
Importance of Privacy
The importance of privacy includes control over information, personal safety, freedom of thought and expression, and more.
Control Over Information: Privacy empowers users to decide what information to share and with whom. Thus, they have autonomy over their personal data. Privacy also protects sensitive data, financial records, or medical histories from falling into the wrong hands.
Freedom of Thought and Expression: Users can freely explore their interests and ideas with assured data privacy. They can also express themselves without any fear of judgment or surveillance. Hence, privacy is crucial for individual belief development and a healthy governance system.
Personal Safety: Privacy is closely connected with a person’s personal safety. Publicly sharing location data can make users vulnerable to stalking, leading to physical and emotional harm. Privacy of communication data saves users from harassment or intimidation.
Identity and Reputation: User privacy allows them to determine their online and offline presence. They can choose how the world may perceive them, and privacy protects them from unwanted exposure to personal information, which harms their reputation.
Benefits of Privacy
Privacy empowers us in many ways, fostering personal growth, mental well-being, innovation, and more.
Personal Growth: With privacy, users get a safe space where they explore thoughts, feelings, and beliefs without any fear of judgment. This is an important benefit of privacy, as it allows self-discovery and new idea development without fear of public scrutiny.
Mental Peace: Privacy allows users to relax and unwind without constantly being under surveillance. It gives them peace without stress and anxiety, leading to mental well-being.
Innovation and Creativity: Sometimes, individuals and businesses must experiment with new ideas and take creative risks. A degree of privacy allows them to do so without fear of immediate public exposure or criticism. This allows them to practice creativity to achieve the desired breakthroughs across various fields.
Healthy Relationships: Users also require privacy at the personal level. Only with the assurance of privacy can one engage in honest and open communication with their loved ones.
Freedom from Discrimination: People often face discrimination in their personal, professional, and social lives because of their choices, beliefs, and past mistakes. Privacy allows them a second chance and the freedom to move on from experiences.
What is Endpoint Security?
Endpoint security is a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that shields endpoint devices such as laptops, desktops, tablets, mobile phones, and IoT devices for home security that connect to a network. Hackers can easily use these devices as entry points to infiltrate a network. Endpoint security protects these endpoints from threats such as malware, phishing attacks, and unauthorized access. It goes beyond traditional methods implemented by antivirus software and uses a multi-layered approach to secure data and systems or organizations.
How Does Endpoint Security Work
Endpoint security protects endpoint devices like laptops, desktops, and mobiles from cyberattacks. In this method, companies usually install software to constantly monitor the activity of these devices. If the software can identify any suspicious behavior or malware, it immediately blocks malicious files from being downloaded or running. It detects unusual attempts to access data or system resources, restricts unauthorized programs from running, and encrypts data to make it unreadable during a breach.
Together with these approaches, endpoint security creates a layered defense, making it significantly harder for attackers to access the device.
Importance of Endpoint Security
Endpoint security is an important foundation for any cybersecurity strategy, safeguarding devices, data, and overall business continuity.
First Line of Defense: Cyberattackers often make endpoints their initial entry points. For this reason, strong endpoint security functions as the first line of defense for organizations that secure their network from unauthorized access, malware, phishing attempts, data theft, and ransomware.
Protecting Sensitive Data: Endpoints often store sensitive data, such as financial records and customer information. Endpoint security solutions use encryption and access control features to prevent data breaches from those devices.
Empowering a Remote Workforce: Due to the rise of remote work, the attack surface for organizations has spread greatly. Endpoint security secures remote employee devices, ensuring they meet security standards and minimizing the risk of unauthorized access to the organizational network.
Improved Response and Recovery: Endpoint security tools offer real-time monitoring and threat detection, allowing businesses faster response times to security incidents. It also minimizes the chances of damage and quickens recovery efforts.
Reduced Risk of Business Disruption: Cyberattacks on endpoint devices can badly disrupt business operations, causing website downtime and lost productivity. With effective endpoint security, companies can prevent these disruptions and continue smooth operations.
Benefits of Endpoint Security
Endpoint security goes beyond basic protection, offering granular control, advanced threat detection, streamlined management, and more.
Granular Control and Visibility: Advanced endpoint security solutions give organizations granular device control. IT teams can customize security policies for different user groups or device categories. These solutions also offer detailed visibility into endpoint activities, allowing IT to identify and respond to suspicious behavior.
Improved Threat Intelligence and Hunting: Endpoint security does not mean having antivirus protection. Modern endpoint security solutions leverage threat intelligence feeds and machine learning to discover emerging threats and zero-day attacks. Thus, organizations can stay ahead of evolving cyber threats and quickly identify potential risks.
Simplified Device Management: Using endpoint security solutions, organizations can have centralized device management capabilities. This saves time and resources for IT teams who can easily deploy security policies, monitor all devices’ security status and activities from a single console, and distribute software updates.
Enhanced User Experience: Endpoint security includes application control and web filtering options that let users block malicious websites and applications. Besides creating a safer browsing environment free from the risk of phishing attacks for users, it helps to minimize disruptions caused by non-work-related activities.
Increased User Confidence: Employees are assured of the security of their devices and can work with greater confidence and peace of mind. This leads to improved productivity and a more focused workforce.
Stronger Overall Security Posture: Endpoint security is essential to a layered security strategy. Organizations can eliminate a major entry point for attackers by securing the endpoints and thus significantly strengthen their overall cybersecurity defense.
What is Password Management?
Password management is the practice of securely storing and creating passwords for all your online accounts. Remembering countless unique passwords is difficult, and reusing the same password across several sites poses a security risk.
Password management resolves all these issues. Usually, password managers handle the entire process of password management, which involves creating unique passwords for various websites and apps, storing them centrally, and autofill them when users want to log in.
How Does Password Management Work
To understand the process of password management, it is important to know how password manager applications work. These programs function as a secure vault where all the passwords and login credentials of different websites are stored. Password managers generate strong yet unique passwords for all the user accounts, so the users do not need to reuse any password twice.
Password managers encrypt passwords before storing them in a central location that can be accessed with a single master password. Most of these applications offer an autofill feature, which automatically enters the login information on websites and apps. Thus, it saves time and frustration for the users. Besides passwords, some applications securely store notes and financial details.
Importance of Password Management
Password management is important for online security, boosting your defenses, reducing data breach risk, and streamlining your digital life.
Enhanced Security: Only strong and unique passwords can ensure online security for individuals and businesses. Password managers create and store separate complex passwords for every account, resulting in reduced risk of hacking and unauthorized access.
Reduced Risk of Data Breach: Many users find creating separate passwords for different accounts difficult. Hence, they resort to using the same password for multiple accounts. If the password of one account gets compromised, all other accounts become susceptible to hacking. Password managers eliminate this risk by ensuring unique passwords for each account.
Convenience and Time-Saving: Nowadays, every website wants users to create user accounts, requiring them to use and remember countless passwords. Password managers securely store the login credentials and free users from remembering them. They can easily access passwords for all online accounts with a single master password.
Improved User Experience: Remembering unique passwords, resetting forgotten passwords, and manually entering long passwords are boring and frustrating tasks. Password managers allow users to eliminate all these problems, ensuring a smooth online experience.
Reduced Phishing Risk: Some password managers also offer additional security features like phishing protection. These offer an extra defense layer against cyberattacks by warning users about suspicious activities and websites.
Benefits of Password Management
Password managers offer a range of benefits beyond just remembering passwords, boosting collaboration, password hygiene, disaster recovery, and overall security posture.
Enhanced Collaboration and Sharing: In a collaborative environment, team members use shared accounts. Password managers ensure secure credential sharing, allowing employees access without compromising their passwords. This streamlines workflows for projects requiring shared access.
Stronger Password Hygiene: Password managers enforce password strength and complexity rules, generate strong, unique passwords, and prompt regular updates. This prevents security vulnerabilities from weak or reused passwords.
Improved Disaster Recovery: Password managers also protect users from losing access to critical accounts, even in cases of lost and damaged devices. Securely storing credentials in the cloud allows easy recovery and continued access from any authorized device.
Simplified Security Audits and Compliance: Many password managers generate reports on password strength, simplifying security audits. They comply with internal security policies during password creation and storage, demonstrating adherence to data security regulations.
Reduced Helpdesk Burden: Organizations often need to contact the IT support of different companies for forgotten passwords. Businesses can significantly reduce these requests using password managers, as all the important passwords are securely stored in a central location.
How Does Cybersecurity Protect Against Cyber Threats?
Cybersecurity utilizes a multi-layered approach that involves both prevention and response strategies. This continuous process requires constant vigilance and adaptation to stay one step ahead of evolving threats.
Preventing Cyber Threats
To proactively ensure security, cybersecurity implements the following cybersecurity controls:
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) and Firewalls: These filter inbound and outbound traffic for suspicious activity. Firewalls block unauthorized access attempts, while IDS/IPS can raise alerts or even block threats automatically by detailed monitoring.
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software: Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software applications proactively scan systems for viruses, worms, malware, spyware, and trojans to quarantine or remove them before infection.
- Encryption: Encryption is a sophisticated method to scramble data and turn it into an unintelligible format. It safeguards sensitive information both while in transit and at rest.
- Strong Passwords: A strong password policy that emphasizes complex combinations of characters makes it harder for hackers to gain access, even if they breach the outer defenses.
- Access Controls: Limiting access to systems and data based on user permissions effectively prevents cyber threats. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security beyond a password by requiring additional verification steps.
- Security Awareness Training: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices, like identifying phishing emails and avoiding suspicious links, is crucial for preventing cybercrime. This works as the first line of defense against social engineering attacks.
Mitigating and Addressing Threats
Below are outlined steps to prevent and address security threats.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM collects security data from various sources to offer a centralized view of security events. Thus, users can initially identify suspicious activities and potential breaches.
- Incident Response Plans: The plan for responding to a cyberattack is critical. This plan outlines threat containment, damage mitigation, and system restoration steps.
- Vulnerability Management: Vulnerability Management approach includes regularly applying security updates with the latest security fixes. It allows users to close exploitable gaps.
- Threat Intelligence: Another proactive defense mechanism is staying informed about the latest cyber threats and attack methods.
- Digital Forensics and Incident Recovery: After a cyberattack, the digital forensics team investigates the incident and collects evidence to determine the scope of the breach. Incident recovery focuses on restoring affected systems and data as early as possible.
Example of Cybersecurity Measures for Cyber Threat: Phishing Email
Below is an example of the cybersecurity measure for the cyber threat.
Cybersecurity Protection
- Email Filtering: Preventive measures like email filtering can block suspicious emails. As it uses sender reputation, keywords, and attachment types to screen incoming emails, less number of emails with phishing attempts reach the inbox.
- User Training: Organizations can educate and train employees to raise awareness about phishing attempts. Thus, they can easily identify phishing attempts by red flags, such as misspelled URLs, requests for personal information, generic greetings, and urgency tactics.
Cybersecurity Response
- Investigation by IT Security: IT security teams should investigate suspicious emails following the due procedure. The investigation includes email header analysis, sender legitimacy verification, and screening of malicious links or attachments.
- Threat Isolation: When a phishing email bypasses filters and compromises a user account, the IT security team can quickly restrict access to sensitive data and systems to isolate the threat.
- Securing Compromised Accounts: The IT team must immediately disable the compromised accounts to prevent further damage. They should take other measures like password reset, adding a strong and unique password, scanning user devices for malware, and recovering from data breaches.
What Are Technologies Used in Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity relies on a diverse range of technologies to defend against ever-evolving threats.
- Firewalls: These monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic to filter out suspicious activity based on predefined security rules. Firewalls are usually software, but these can also be hardware or a combination.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems monitor network traffic and system activity continuously to determine signs of malicious behavior. An IDS shares alerts on potential threats, while an IPS can actively block them.
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software: These applications scan devices to identify viruses, malware, spyware, worms, trojans, and ransomware. Their main task is to quarantine or remove threats and prevent them from infecting the system.
- Encryption: This popular technology makes any data unreadable unless the reader has the key to decrypt it. Encryption can protect sensitive information both in transit and at rest.
- Access Control: This approach limits access to systems and data based on user permissions. It ensures that only authorized personnel have access to the information.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): This technology prevents accidental or intentional leakage of sensitive data from an organization.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM aggregates security data from various sources to share a centralized view of security events and potential threats across an organization.
- AI and ML: These comparatively new technologies address increasingly sophisticated threats. Their use is seen in threat detection and analysis, behavioral biometrics, and blockchain for secure data storage and sharing.
Is There a Job for Cybersecurity?
Yes, there are many jobs in cybersecurity. The surge in cyber threats and the continuous expansion of the digital landscape have propelled cybersecurity into a high-growth job market. This booming demand results in a wealth of cybersecurity jobs catering to individuals with various backgrounds and skill sets. Most organizations actively recruit cybersecurity professionals to strengthen their defenses and protect vital data and systems from cyber-attacks.
How Does Cybersecurity Differ from Traditional Security Measures?
Traditional security protects physical or tangible assets through physical barriers and access control. On the other hand, cybersecurity protects digital information, systems, and networks from cyberattacks. Here is a breakdown of the key differences between traditional security and cybersecurity.
| Traditional Security | Cybersecurity | |
|---|---|---|
| Threats | Theft, vandalism, and unauthorized access | Malware, hacking, and data breaches |
| Solutions | Locks, alarms, and security personnel | Firewalls, antivirus, intrusion detection systems, and encryption |
| Focus | Protection of physical assets | Protecting digital assets and information |
| Scalability | Limited scalability | Easily scalable |
| Working Method | Physical observation and reports | Monitoring systems and data analysis |
| Integration | No integration support | Integration possible with other security measures |
What Are Some Common Misconceptions about Cybersecurity?
The business world is full of misconceptions about cybersecurity. The following list includes the most common myths that can lead to business risk.
- Hackers target only the important people or large companies.
- Strong antivirus software gives you complete protection against cybercrime.
- Public Wi-Fi with a password is safe to use.
- A complex password is enough to keep someone safe.
- It is not mandatory to update the software or apps regularly.
- Clicking on a suspicious link will not cause any harm unless the user downloads it.
- Mac devices are not susceptible to viruses.
- Cybersecurity is the responsibility of IT professionals only.
- Security software slows down the devices.
- Regulatory compliance guarantees the security of the entire system.
- Organizations can ensure complete security by regular penetration testing.
- Cloud platforms manage security needs.
- Free Wi-Fi is safe when used with a VPN.
- Phishing emails are always easy to spot.
- Cybersecurity is too complicated for general users to understand.
What is the Role of Cybersecurity in Information Technology?
While IT is an indispensable part of today’s digital world, it comes with a growing risk for cyberattacks. The role of cybersecurity is highly critical in information technology (IT). Let’s explore how cybersecurity safeguards IT.
Protect Sensitive Information
IT systems consist of a large volume of financial records, intellectual property, and customer information. A data breach can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and even legal repercussions. Cybersecurity shields this data from unauthorized access, theft, or corruption.
Ensure System Availability
Cyberattacks often disrupt IT systems by preventing users from accessing critical applications and data. Such outage cripples business operations and team productivity. Cybersecurity approaches like firewalls and intrusion detection systems stop these attacks from happening and keep these systems available.
Maintain Data Integrity
Malicious elements tamper with IT systems to manipulate data or disrupt regular operations. Cybersecurity ensures data integrity by protecting systems from unauthorized modifications. This role is important for finance and healthcare industries, where the value of data accuracy is paramount.
Build Trust
Strong cybersecurity means the organization is committed to protecting sensitive information. It builds trust with customers, partners, and investors while maintaining a good reputation.
Data empowers organizations to make informed decisions at every level of operations. It does so by revealing trends, customer behavior, and room for improvement. It offers businesses a significant competitive edge so that they can develop innovative products, provide personalized experiences, and optimize operations. Furthermore, data analysis streamlines automated tasks and identifies cost-saving opportunities. Ultimately, data acts as a starting point for innovation.
What Is Cybersecurity Mesh?
Cybersecurity mesh is a type of security architecture that creates a distributed web of security controls for the network. This approach is different from the traditional perimeter-based defense that builds a single wall around the entire network. The security controls of cybersecurity mesh involve security software, firewalls, and other tools on individual devices and applications.
In cybersecurity mesh, all controls communicate with each other to share threat intelligence. Thus, organizations get a more dynamic and adaptable security framework. Even if any part of the mesh is compromised, the others continue to function and limit the damage. Cybersecurity mesh is most appropriate for modern, cloud-based environments where data and applications are located in different locations.
What are AI-Powered Cybersecurity Platforms That Can Be Integrated to Your Organization?
Organizations can integrate these AI cybersecurity platforms to protect data, applications, and services against cyberattacks.
- Darktrace: protects an enterprise’s digital assets, analyzes network data threats, tracks email phishing and screens cloud environment threats with its Enterprise Immune System. Its self-learning AI learns from daily operations to apply them to visualize and correlate security incidents.
- CrowdStrike Falcon: a cloud protection software that does threat hunting and proactive prevention of breaches.
- SentinelOne: a threat-hunting platform that detects, responds to, and prevents cybersecurity attacks.
What is the Difference Between Cybersecurity and Cyber Resilience?
Cybersecurity and cyber resilience focus on different stages of a cyberattack. Cybersecurity functions as a shield that prevents cyberattacks, while cyber resilience allows users to bounce back after an event of cyberattack.
Cybersecurity utilizes relevant tools and best practices, like firewalls and encryption, to actively defend systems and data. Unlike traditional cybersecurity, cyber resilience takes a broader approach. The approach includes disaster recovery plans, employee training, and incident response protocols to enable organizations to bounce back from an attack.

